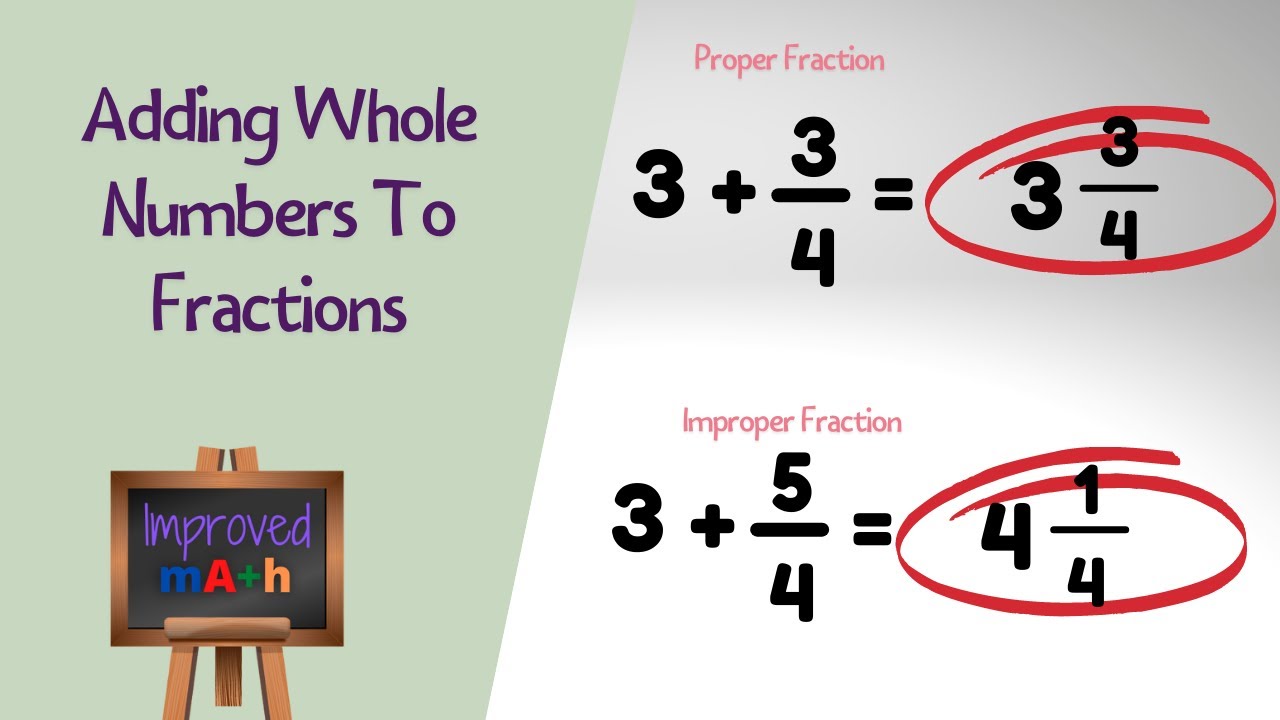
Understanding how to perform addition with fractions and whole numbers is essential for students and anyone looking to enhance their mathematical skills. This topic can be a bit challenging at first, but with the right guidance, you can master it in no time. In this article, we will explore the concepts of adding fractions to whole numbers, provide practical examples, and discuss common mistakes to avoid. Whether you are a student, a teacher, or just someone wanting to brush up on their math skills, this guide is for you.
We will begin by breaking down the basics of fractions and whole numbers, followed by detailed steps on how to add them effectively. Additionally, we’ll include tips and tricks to simplify your calculations. Our goal is to empower you with knowledge so that you feel confident in your ability to tackle addition involving fractions and whole numbers.
By the end of this article, you will not only know how to add fractions to whole numbers but also understand the underlying principles that govern these mathematical operations. So, let’s dive in and explore this essential topic!
Table of Contents
- 1. Understanding Fractions
- 2. Understanding Whole Numbers
- 3. Adding Fractions and Whole Numbers
- 4. Examples of Addition with Fractions and Whole Numbers
- 5. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 6. Practical Tips for Success
- 7. Conclusion
1. Understanding Fractions
Fractions represent a part of a whole and consist of two components: the numerator (the top number) and the denominator (the bottom number). For instance, in the fraction ¾, 3 is the numerator and 4 is the denominator. Understanding how fractions work is crucial for performing addition with them.
2. Understanding Whole Numbers
Whole numbers are non-negative integers that do not include fractions or decimals. They begin from zero and go on infinitely (0, 1, 2, 3, ...). Whole numbers are straightforward and form the basis for many mathematical operations.
3. Adding Fractions and Whole Numbers
When adding fractions to whole numbers, you must follow a few steps to ensure accuracy. Here’s how to do it:
3.1 Converting Fractions
Before you can add a fraction to a whole number, it’s often helpful to convert the whole number into a fraction. You can do this by placing the whole number over 1. For example, to add the whole number 5 to the fraction ¾, you would convert 5 to 5/1.
3.2 Finding Common Denominators
If the fractions you are working with have different denominators, find a common denominator. This will allow you to add the fractions together easily. In our example, to add 5/1 and ¾, the common denominator would be 4.
4. Examples of Addition with Fractions and Whole Numbers
Let’s look at some practical examples to solidify our understanding:
- Example 1: 5 + ¾ = 5/1 + ¾ = 20/4 + 3/4 = 23/4
- Example 2: 2 + ⅗ = 2/1 + ⅗ = 6/3 + ⅗ = 6/3 + 3/3 = 9/3 = 3
5. Common Mistakes to Avoid
When adding fractions and whole numbers, students often make mistakes. Some common pitfalls include:
- Forgetting to convert whole numbers to fractions
- Not finding a common denominator when necessary
- Adding the numerators and denominators incorrectly
6. Practical Tips for Success
Here are some tips to help you succeed in adding fractions and whole numbers:
- Always convert whole numbers to fractions to simplify calculations.
- Practice finding common denominators to make addition easier.
- Double-check your work for accuracy.
7. Conclusion
In summary, addition with fractions and whole numbers is a fundamental skill that can be mastered with practice. We covered the essential steps, provided examples, and discussed common mistakes to avoid. Now that you have a clearer understanding, we encourage you to practice these techniques on your own.
Feel free to leave a comment, share this article, or explore more of our resources on mathematical concepts. Your journey to mastering math is just beginning!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back here for more insightful articles!
Article Recommendations
- Data Driven_0.xml
- Daryl Hannah
- Nikki Minja Naked
- Three Cornered Hat Crossword Clue
- Japanese Watch Brands
- Claudine Blanchard Crimes
- Mario Lopez
- Non Fiction Meaning
- Chevy S10 Steering Wheel
- Corinne Foxx