Data is the backbone of analytical processes across various fields, from business to science. Understanding the difference between categorical and numerical data is crucial for data analysis, interpretation, and reporting. In this article, we will explore these two fundamental types of data, their characteristics, and their applications. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to differentiate between them and why it matters in data-driven decision-making.
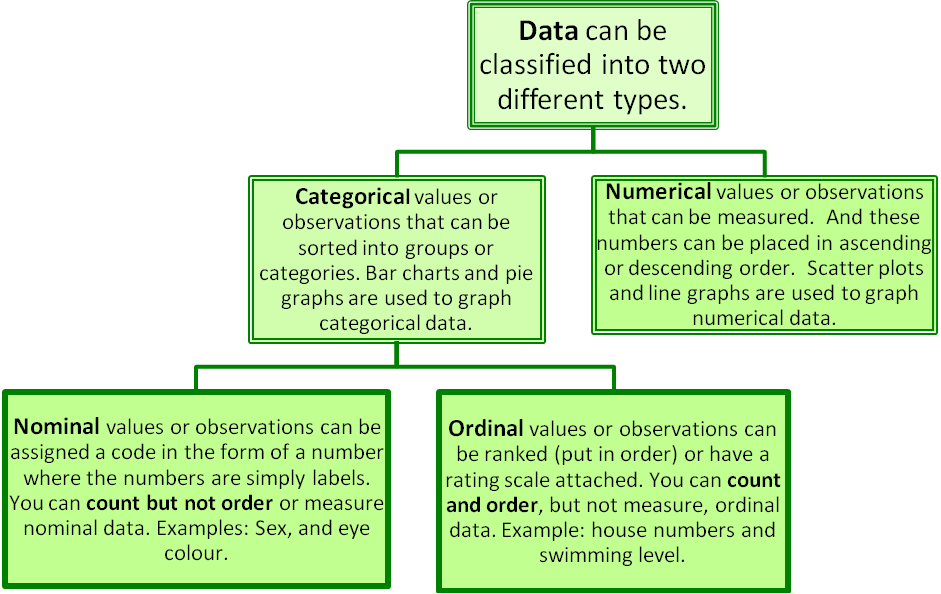
Data can generally be classified into two main types: categorical data and numerical data. Categorical data refers to variables that represent categories or groups, while numerical data consists of numbers that can be quantified. Each type has its unique properties, uses, and implications in statistical analysis. Understanding these differences can significantly enhance your ability to analyze and interpret data effectively.
In today's data-centric world, being able to categorize and analyze data correctly is essential for making informed decisions. Whether you are a student, a business analyst, or a researcher, grasping these concepts will improve the quality of your work. So let’s dive deeper into the differences between categorical and numerical data.
Table of Contents
- Definition of Categorical and Numerical Data
- Characteristics of Categorical Data
- Characteristics of Numerical Data
- Examples of Categorical and Numerical Data
- Statistical Analysis of Categorical and Numerical Data
- Data Visualization Techniques
- Applications in Real-World Scenarios
- Conclusion
Definition of Categorical and Numerical Data
Categorical data refers to variables that can be divided into groups or categories. These categories can be qualitative in nature, meaning they do not have a quantitative value. For example, categories such as "gender," "color," or "type of pet" are all examples of categorical data.
On the other hand, numerical data represents measurable quantities. This type of data can be further divided into two sub-types: discrete and continuous data. Discrete data can take on a finite number of values (e.g., the number of students in a classroom), while continuous data can take on an infinite number of values within a given range (e.g., height or weight).
Characteristics of Categorical Data
Categorical data has several key characteristics:
- Qualitative Nature: Categorical data represents attributes or qualities.
- Non-Numeric: The values are usually words or labels.
- Limited Scope: Categorical variables can have a limited number of categories.
- No Mathematical Operations: You cannot perform mathematical operations like addition or subtraction on categorical data.
Characteristics of Numerical Data
Numerical data has distinct characteristics as well:
- Quantitative Nature: Numerical data represents quantities and measurements.
- Numeric Values: The values are numbers that can be manipulated mathematically.
- Infinite Possibilities: Especially in the case of continuous data, the range of values can be infinite.
- Mathematical Operations: You can perform various mathematical operations on numerical data.
Examples of Categorical and Numerical Data
Categorical Data Examples
- Colors of cars (red, blue, green)
- Types of fruits (apple, banana, orange)
- Marital status (single, married, divorced)
Numerical Data Examples
- Age of individuals (in years)
- Temperature readings (in degrees)
- Income levels (in dollars)
Statistical Analysis of Categorical and Numerical Data
Statistical analysis methods differ for categorical and numerical data:
- Categorical Data Analysis: Techniques such as chi-square tests, mode calculations, and contingency tables are used.
- Numerical Data Analysis: Methods like mean, median, standard deviation, and regression analysis are commonly applied.
Data Visualization Techniques
Visualization is essential for interpreting both categorical and numerical data:
- Categorical Data Visualization: Bar charts, pie charts, and frequency tables are effective for displaying categorical data.
- Numerical Data Visualization: Histograms, box plots, and scatter plots are commonly used for numerical data.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
Understanding the difference between categorical and numerical data has practical applications in various fields:
- Business: Analyzing customer demographics (categorical) and sales figures (numerical) helps businesses make informed decisions.
- Healthcare: Studying patient categories (categorical) and their medical costs (numerical) aids in resource allocation.
- Education: Evaluating student performance (numerical) and their backgrounds (categorical) enriches educational strategies.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the difference between categorical and numerical data is vital for effective data analysis. Categorical data helps categorize information, while numerical data provides measurable metrics. By leveraging these two types of data appropriately, you can enhance the accuracy and relevance of your analyses, leading to better decision-making.
We encourage you to explore more about data types and their analysis. Feel free to leave a comment or share this article with others who might benefit from it. For further reading, check out our other articles on data analysis and visualization.
Thank you for reading! We hope to see you back on our site for more insightful articles.
Article Recommendations
- Three Cornered Hat Crossword Clue
- Kamila Valieva
- 76 Out Of 80
- Convert Excel To Html Table
- Active Smooth Nail Polish
- Travis Kelce August 2024
- Financial Empowerment_0.xml
- Outdoor Propane Heater Table Top
- Business Tactics_0.xml
- Jennifer Syme Crash