The concept of limits to infinity rules is fundamental in calculus and mathematical analysis. These rules help in understanding how functions behave as they approach infinity, which is crucial for solving various mathematical problems. By mastering these concepts, you can enhance your problem-solving skills and gain a deeper understanding of advanced mathematics.
In this article, we will explore the limits to infinity rules in detail, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of the topic. We will cover various aspects, including the significance of limits, different types of functions, and practical applications of these rules. Whether you are a student, educator, or math enthusiast, this guide will serve as a valuable resource for deepening your knowledge.
As we delve into the intricacies of limits to infinity, we will also highlight key examples and provide clear explanations to ensure that the information is accessible and easy to comprehend. By the end of this article, you will have a solid grasp of the limits to infinity rules and their implications in various mathematical contexts.
Table of Contents
- What are Limits to Infinity?
- Importance of Limits in Calculus
- Types of Functions and Their Limits
- Rules for Calculating Limits to Infinity
- Examples of Limits to Infinity
- Applications of Limits to Infinity
- Common Misconceptions about Limits
- Summary and Call to Action
What are Limits to Infinity?
Limits to infinity refer to the behavior of a function as the input approaches infinity or negative infinity. In other words, it describes what happens to the value of a function when the variable grows larger and larger without bound. Understanding these limits is crucial for analyzing the end behavior of functions, especially in calculus.
Importance of Limits in Calculus
The concept of limits is foundational in calculus and serves as the basis for defining derivatives and integrals. Here are some key reasons why limits are essential:
- They provide insight into the behavior of functions at extreme values.
- Limits help in evaluating indeterminate forms, such as 0/0 or ∞/∞.
- They are crucial for understanding continuity and differentiability of functions.
- Limits form the basis for defining important concepts like asymptotes and infinite series.
Types of Functions and Their Limits
Different types of functions exhibit distinct behaviors as they approach infinity. Here are some common function types:
- Polynomial Functions: The limits of polynomial functions at infinity are determined by the leading term.
- Rational Functions: The limits depend on the degrees of the numerator and denominator.
- Exponential Functions: These functions grow rapidly, and their limits at infinity are typically infinite.
- Logarithmic Functions: These functions grow slowly, and their limits at infinity approach infinity, albeit at a slower rate.
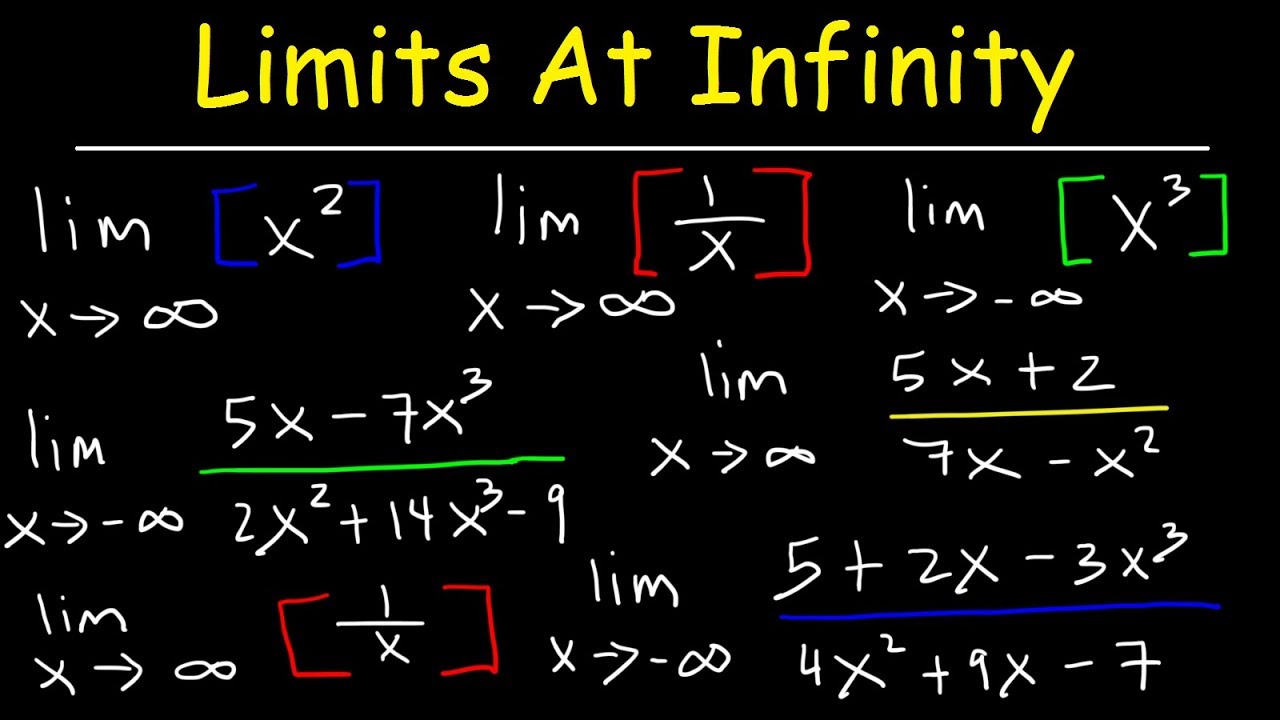
Rules for Calculating Limits to Infinity
When calculating limits to infinity, several rules can simplify the process:
1. Limit of a Constant
The limit of a constant as x approaches infinity is simply the constant itself.
2. Polynomial Limits
For polynomial functions, the limit is determined by the highest degree term. For example:
- As x approaches infinity, the limit of f(x) = 3x^3 + 2x^2 + 5 approaches infinity.
3. Rational Functions
For rational functions, compare the degrees of the numerator and denominator:
- If the degree of the numerator is greater, the limit is infinity.
- If the degree of the denominator is greater, the limit is 0.
- If the degrees are equal, the limit is the ratio of the leading coefficients.
4. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
Exponential functions tend to grow faster than polynomial functions, while logarithmic functions approach infinity but at a slower rate. Understanding these behaviors is essential for calculating limits accurately.
Examples of Limits to Infinity
Let's explore some examples to illustrate the application of limits to infinity rules:
- Example 1: Determine the limit of f(x) = 5x^2 + 3x as x approaches infinity.
- Solution: The limit is infinity since the leading term dominates.
- Example 2: Find the limit of g(x) = (2x^2 + 3)/(4x^2 + 5) as x approaches infinity.
- Solution: The limit is 1/2, as the degrees of the numerator and denominator are equal.
Applications of Limits to Infinity
Understanding limits to infinity has several practical applications, including:
- Analyzing the end behavior of functions in calculus.
- Determining horizontal asymptotes in graphing functions.
- Solving real-world problems involving growth rates, such as population growth or radioactive decay.
Common Misconceptions about Limits
Despite the importance of limits, there are several misconceptions that can lead to confusion:
- Limits do not always exist; it's essential to analyze the behavior of the function carefully.
- Approaching infinity does not mean reaching a specific value.
- Indeterminate forms require special techniques for evaluation.
Summary and Call to Action
In summary, limits to infinity rules are crucial for understanding the behavior of functions in calculus. By mastering these concepts, you can enhance your mathematical skills and apply them to various problems. We encourage you to practice calculating limits and explore their applications in real-world scenarios.
If you found this article helpful, please leave a comment below, share it with your peers, or explore our other articles for more insights into advanced mathematics!
Conclusion
Thank you for taking the time to read this comprehensive guide on limits to infinity rules. We hope you gained valuable insights and feel more confident in your understanding of this essential mathematical concept. Don't hesitate to return for more informative articles and discussions!
Article Recommendations
- Claudine Blanchard Crimes
- Poker Face Sunglasses
- Kill Fleas In House
- Legal Seafood Recipes Crab Cakes
- Clothes Not Smelling Fresh After Washing
- Debutante
- Deacon Johnson
- 76 Out Of 80
- Bang On Casino
- Chevy S10 Steering Wheel