Triangles are fundamental shapes in geometry, and understanding their properties is crucial for students and professionals alike. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of triangles, focusing specifically on their interior and exterior angles. This knowledge is not only essential for academic purposes but also has practical applications in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and design.
Triangles are defined by their three sides and three angles, and they can be categorized based on their angles and sides. The study of angles in triangles helps us unlock the secrets of their properties and relationships. In this article, we will explore the definitions, properties, and theorems related to interior and exterior angles of triangles, providing a comprehensive overview of this essential topic.
By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of how to calculate and apply the concepts of interior and exterior angles in triangles. Whether you are a student preparing for an exam or a professional seeking to refresh your knowledge, this guide will serve as a valuable resource.
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Triangles
- 2. Understanding Interior Angles
- 3. The Interior Angle Theorem
- 4. Understanding Exterior Angles
- 5. The Exterior Angle Theorem
- 6. Applications of Triangle Angles
- 7. Examples and Practice Problems
- 8. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Triangles
Triangles are one of the simplest yet most important shapes in geometry. They have three sides and three angles, and they can be classified into various types based on the length of their sides and the measurement of their angles.
There are three main types of triangles based on their angles:
- Acute Triangle: All angles are less than 90 degrees.
- Right Triangle: One angle is exactly 90 degrees.
- Obtuse Triangle: One angle is greater than 90 degrees.
Triangles can also be categorized by the lengths of their sides:
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are equal in length.
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are of equal length.
- Scalene Triangle: All sides are of different lengths.
2. Understanding Interior Angles
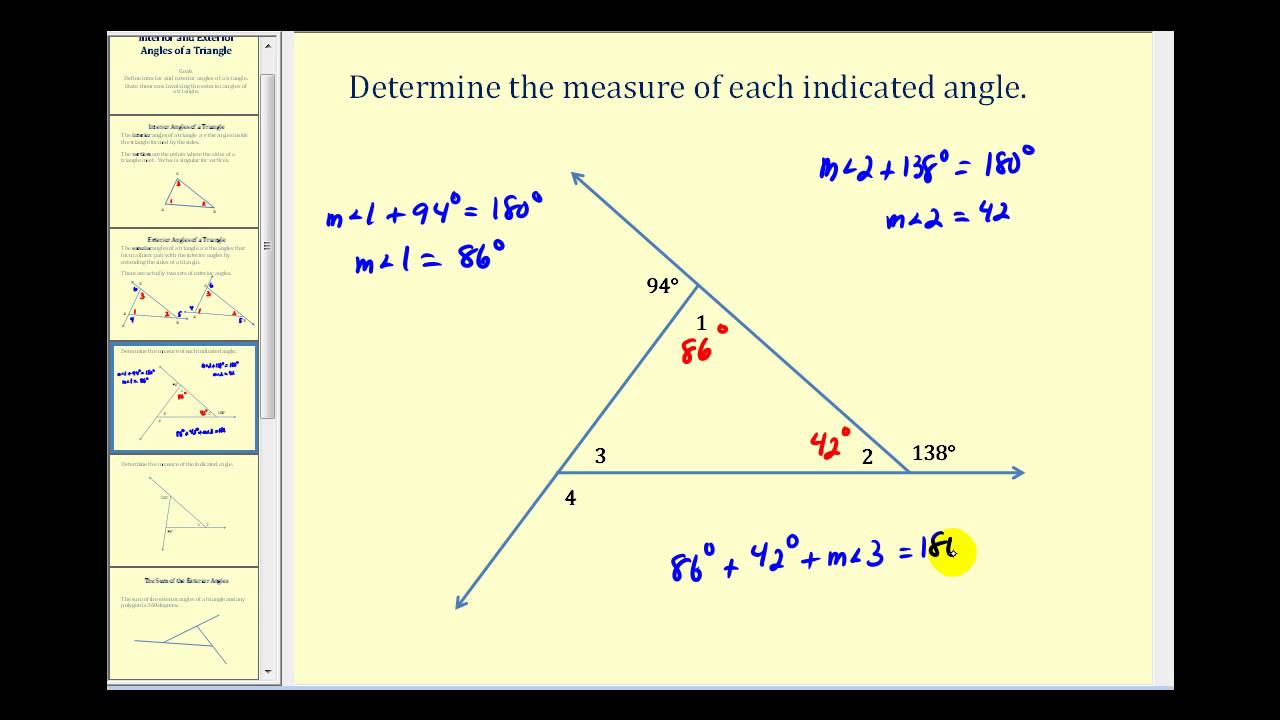
The interior angles of a triangle are the angles formed inside the triangle by the intersection of its sides. The sum of the interior angles in any triangle is always equal to 180 degrees. This fundamental property is essential for solving various geometric problems.
Properties of Interior Angles
- The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
- Each angle can be calculated if the other two angles are known.
- In an equilateral triangle, each interior angle measures 60 degrees.
3. The Interior Angle Theorem
The Interior Angle Theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is equal to 180 degrees. This theorem is foundational in geometry and is often used to solve problems involving triangles.
For example, if a triangle has two angles measuring 50 degrees and 70 degrees, the third angle can be calculated as follows:
Third Angle = 180 - (50 + 70) = 60 degrees.
4. Understanding Exterior Angles
Exterior angles of a triangle are formed when a side of the triangle is extended. Each exterior angle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles. Understanding exterior angles is crucial for various applications in geometry.
Properties of Exterior Angles
- The measure of each exterior angle is equal to the sum of the two non-adjacent interior angles.
- The sum of the exterior angles of a triangle is always equal to 360 degrees.
5. The Exterior Angle Theorem
The Exterior Angle Theorem states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two opposite interior angles. This theorem is useful for finding unknown angles in a triangle.
For instance, if one exterior angle measures 120 degrees, the two corresponding interior angles can be calculated using the theorem:
Interior Angle 1 + Interior Angle 2 = 120 degrees.
6. Applications of Triangle Angles
Understanding the properties of interior and exterior angles in triangles has practical applications in various fields, including:
- Architecture: Designing structures that require precise angles.
- Engineering: Calculating forces and stresses in triangular structures.
- Computer Graphics: Creating realistic 3D models and animations.
7. Examples and Practice Problems
Let's look at some examples to reinforce the concepts we've discussed:
- Example 1: Calculate the third angle of a triangle with interior angles of 30 degrees and 70 degrees.
- Example 2: If one exterior angle of a triangle measures 110 degrees, what are the measures of the two opposite interior angles?
8. Conclusion
In this article, we explored the concepts of interior and exterior angles in triangles, along with the theorems that govern them. We learned that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees, and that exterior angles relate to the opposite interior angles. This knowledge is fundamental in geometry and has numerous applications in the real world.
We encourage you to leave comments, share this article with others, or read more articles on related topics to enhance your understanding of geometry.
References
- Euclidean Geometry, "The Sum of Angles in a Triangle." Retrieved from [source].
- Mathematics Textbook, "Triangles and Their Properties." Retrieved from [source].
- Geometry Online Resources, "Understanding Angles in Triangles." Retrieved from [source].
Article Recommendations
- Best True Story Movies
- Galaxy Playdough
- Risk Territory Between Ukraine And Siberia Nyt
- Business Tactics_0.xml
- Tumblr Fashion Male
- Long Handled Post Hole Diggers
- Lava Stone Bracelet Essential Oil
- Creative Solutions_0.xml
- Business Resilience_0.xml
- Streaming Device Whose Name Means Six