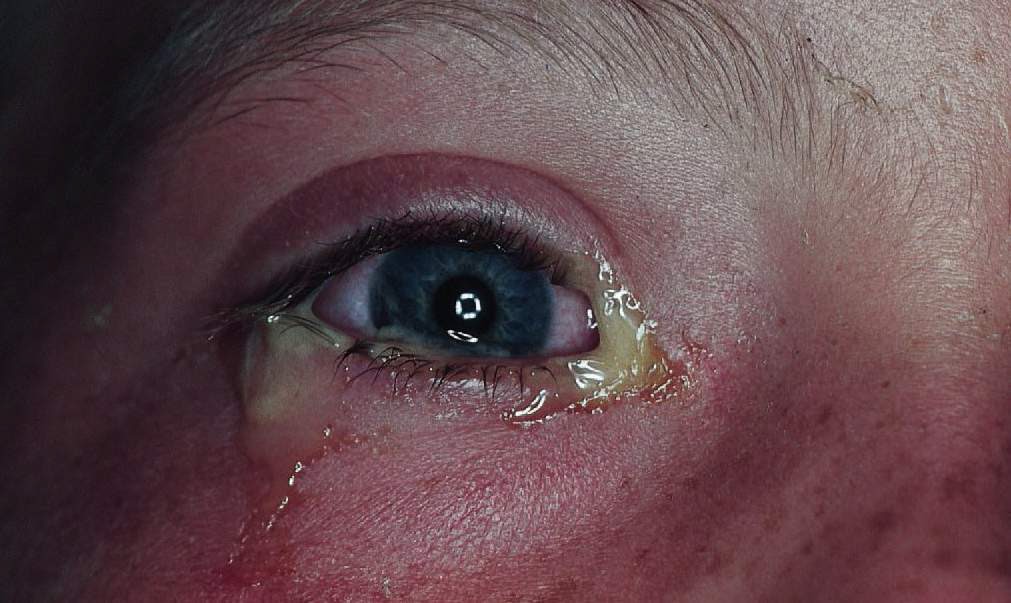
Bacterial conjunctivitis, commonly known as pink eye, is an infection that affects the outer membrane of the eyeball and the inner eyelid. This condition is typically caused by bacteria, leading to symptoms such as redness, irritation, and discharge from the eye. Among the various treatment options available, Tobramycin has emerged as a widely used antibiotic for managing bacterial conjunctivitis. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and the effectiveness of Tobramycin in treating this prevalent eye condition.
Understanding bacterial conjunctivitis is essential, not just for those directly affected, but also for caregivers and healthcare professionals. With its contagious nature, bacterial conjunctivitis can spread easily among individuals, making awareness and prompt treatment crucial. Tobramycin, as an antibiotic eye drop, plays a significant role in combating this infection, helping to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
Throughout this article, we will delve into the specifics of bacterial conjunctivitis and the role Tobramycin plays in its treatment. We'll also highlight important considerations for use, potential side effects, and when to seek further medical attention. Whether you are a patient, a caregiver, or simply seeking information, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into managing bacterial conjunctivitis effectively.
Table of Contents
- What is Bacterial Conjunctivitis?
- Causes and Symptoms
- Diagnosis of Bacterial Conjunctivitis
- Treatment Options for Bacterial Conjunctivitis
- Tobramycin: An Overview
- How Tobramycin Works
- Potential Side Effects of Tobramycin
- When to See a Doctor
- Conclusion
What is Bacterial Conjunctivitis?
Bacterial conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin membrane that covers the white part of the eyeball and the inside of the eyelids. This condition can occur when bacteria infect the conjunctiva, leading to symptoms that may include:
- Redness in the white part of the eye
- Increased tear production
- Discharge that can cause the eyelids to stick together
- Itching or burning sensation
It is important to differentiate bacterial conjunctivitis from other types of conjunctivitis, such as viral or allergic conjunctivitis, as the treatment methods can differ significantly.
Causes and Symptoms
Bacterial conjunctivitis can be caused by several types of bacteria, including:
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenzae
These bacteria can easily spread through direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces, leading to outbreaks in schools or communities.
Symptoms of Bacterial Conjunctivitis
The symptoms of bacterial conjunctivitis typically develop rapidly and can include:
- Redness in one or both eyes
- Thick yellow or green discharge
- Crusty eyelids upon waking
- Swollen eyelids
- Sensitivity to light
Diagnosis of Bacterial Conjunctivitis
A healthcare professional can diagnose bacterial conjunctivitis through a thorough eye examination and by reviewing the patient's symptoms. In some cases, a laboratory test may be performed to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection, particularly if the condition is severe or does not respond to standard treatment.
Treatment Options for Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Treatment for bacterial conjunctivitis primarily involves the use of antibiotic eye drops or ointments. Common antibiotics prescribed include:
- Tobramycin
- Gentamicin
- Ofloxacin
These antibiotics help eliminate the infection and reduce symptoms, typically resulting in improvement within a few days of starting treatment.
Tobramycin: An Overview
Tobramycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that is commonly used to treat bacterial infections, particularly those affecting the eyes. It is effective against a range of bacteria that cause conjunctivitis and is available in the form of eye drops or ointments.
Here is a brief overview of Tobramycin:
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Class | Aminoglycoside antibiotic |
| Indications | Bacterial conjunctivitis |
| Administration | Topical (eye drops or ointment) |
| Common Side Effects | Eye irritation, redness, itching |
How Tobramycin Works
Tobramycin works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, which is crucial for bacterial growth and reproduction. By targeting the ribosomal machinery of bacteria, Tobramycin effectively halts the infection, allowing the body's immune system to eliminate the remaining bacteria.
Potential Side Effects of Tobramycin
While Tobramycin is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience side effects, including:
- Temporary stinging or burning sensation in the eye
- Redness or itching of the eye
- Dry eyes
If any severe side effects occur, such as persistent eye pain or vision changes, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
When to See a Doctor
It is advisable to see a doctor if:
- Symptoms worsen or do not improve within a few days of treatment
- Vision is affected
- There is severe pain in the eye
Early intervention can help prevent complications and ensure effective treatment.
Conclusion
Bacterial conjunctivitis is a common yet manageable condition that requires awareness and appropriate treatment. Tobramycin has proven to be an effective antibiotic in treating this infection, helping alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. If you suspect you have bacterial conjunctivitis, it is essential to seek medical advice promptly and follow the prescribed treatment regimen. Don't hesitate to share your experiences or ask questions in the comments below, and consider exploring more articles on eye health and related topics.
Call to Action
If you found this article helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. For more eye health tips and resources, explore our website for additional articles.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you again soon!
Article Recommendations
- Cost To Extend Garage
- Exterior Joint Compound
- Kylie Jenner Before Surgery
- Growth Hacking_0.xml
- Lava Stone Bracelet Essential Oil
- Metal Worker
- Digital Revolution_0.xml
- Mia Hamm Soccer Player
- Best True Story Movies
- Risk Territory Between Ukraine And Siberia Nyt