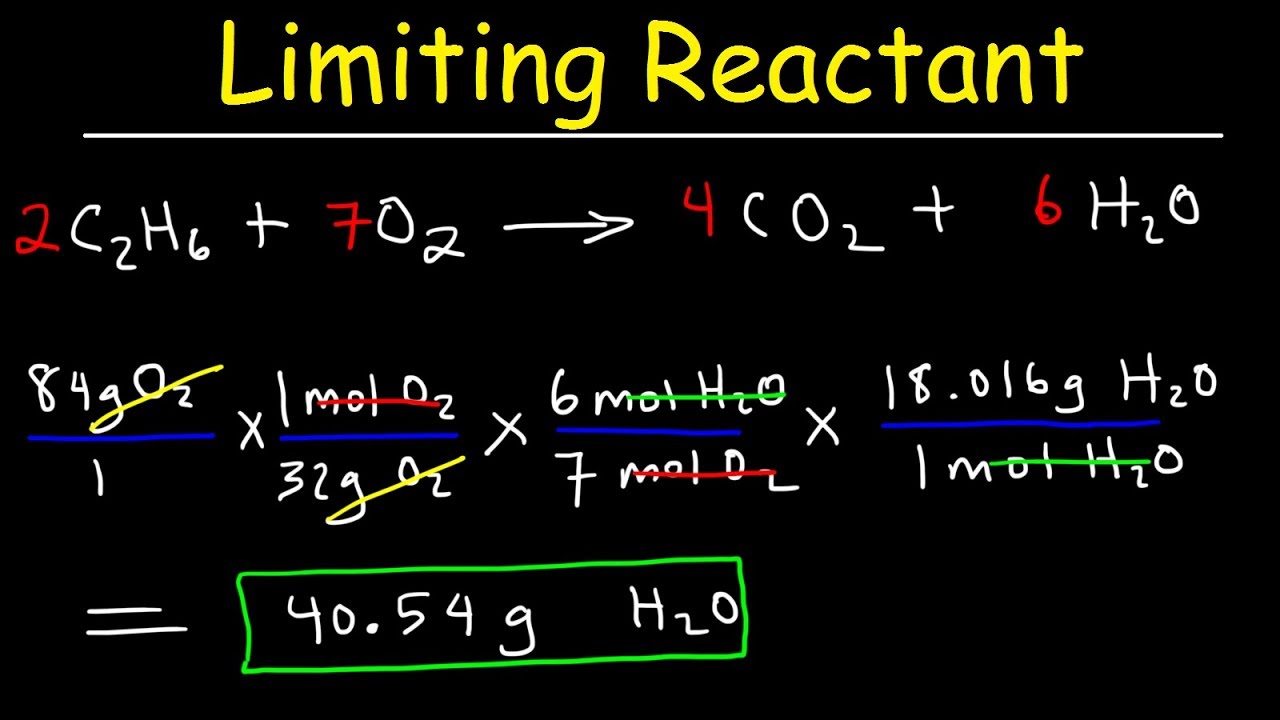
Understanding the concept of limiting reagents is crucial for anyone studying chemistry, whether in a classroom or a lab setting. A limiting reagent is the substance that is totally consumed when the chemical reaction goes to completion. It is important to accurately calculate the limiting reagent to determine the maximum amount of product that can be formed from a given set of reactants. In this article, we will explore what limiting reagents are, how to calculate them, and the importance of using a limiting reagents calculator.
The calculation of limiting reagents is a fundamental skill in chemistry that can greatly affect the outcomes of experiments and reactions. By using a limiting reagents calculator, students and professionals alike can streamline their work and increase accuracy in their results. This guide will provide step-by-step instructions on how to use these calculators effectively, along with practical examples to illustrate their application.
Furthermore, we will delve into the principles behind limiting reagents and discuss common pitfalls to avoid during calculations. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of limiting reagents and the tools available to help you calculate them accurately. Let's get started!
Table of Contents
- What is a Limiting Reagent?
- Importance of Limiting Reagents
- How to Identify Limiting Reagents
- Limiting Reagents Calculator
- Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Limiting Reagents Calculator
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Conclusion
What is a Limiting Reagent?
A limiting reagent is a reactant in a chemical reaction that is consumed first, limiting the amount of product that can be formed. In any chemical reaction, reactants are combined in specific ratios, and if one of the reactants is present in a smaller amount than required, it becomes the limiting reagent.
For example, consider the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water:
- 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
In this reaction, if you have 4 moles of hydrogen and only 1 mole of oxygen, oxygen is the limiting reagent because it will be used up before all of the hydrogen can react.
Importance of Limiting Reagents
Understanding limiting reagents is essential for several reasons:
- It helps in calculating the theoretical yield of products.
- It ensures efficient use of reactants and reduces waste.
- It is critical for industrial processes where cost-effectiveness is important.
- It aids in designing experiments in a laboratory setting.
How to Identify Limiting Reagents
To identify the limiting reagent, follow these steps:
- Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
- Convert the amounts of reactants to moles if they are not already.
- Use the stoichiometric coefficients from the balanced equation to determine how many moles of each reactant are needed.
- Compare the available moles of each reactant to the required moles to see which one runs out first.
Limiting Reagents Calculator
A limiting reagents calculator is a tool that simplifies the process of finding the limiting reagent in a chemical reaction. These calculators can take the quantities of reactants and automatically determine which one is limiting, as well as the theoretical yield of the products.
Many online calculators are available, and they usually require you to input the following information:
- The balanced chemical equation.
- The initial amounts of each reactant (in moles or grams).
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Limiting Reagents Calculator
Here’s how to use a limiting reagents calculator effectively:
- Find a reliable limiting reagents calculator online.
- Input the balanced equation for your reaction.
- Enter the amounts of each reactant you have.
- Submit your information and read the results.
Make sure to double-check your entries to avoid errors in the calculations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating limiting reagents, be aware of these common mistakes:
- Not balancing the chemical equation correctly.
- Using incorrect units (grams instead of moles, for example).
- Failing to convert measurements when necessary.
- Overlooking the stoichiometric ratios required by the reaction.
Examples and Practice Problems
Let’s look at an example to illustrate how to calculate the limiting reagent:
Consider the reaction:
- 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
If you have 3 moles of H2 and 1 mole of O2, you can identify the limiting reagent:
- From the balanced equation, 2 moles of H2 react with 1 mole of O2.
- For 3 moles of H2, you would need 1.5 moles of O2.
- Since you only have 1 mole of O2, it is the limiting reagent.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ability to identify and calculate limiting reagents is a vital skill in chemistry that enhances our understanding of chemical reactions. A limiting reagents calculator can greatly simplify this process, allowing for more accurate and efficient experimentation. Remember to always double-check your calculations and ensure your chemical equations are balanced. If you have any questions or would like to share your experiences with limiting reagents, feel free to leave a comment below!
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights and practical knowledge about limiting reagents and their calculators. Don’t hesitate to explore more articles on our site for further learning!
Article Recommendations
- Nikki Minja Naked
- Chevy S10 Steering Wheel
- Active Smooth Nail Polish
- Clothes Not Smelling Fresh After Washing
- Hig Roberts
- Lava Stone Bracelet Essential Oil
- Deacon Johnson
- Long Handled Post Hole Diggers
- Global Impact_0.xml
- Galaxy Playdough