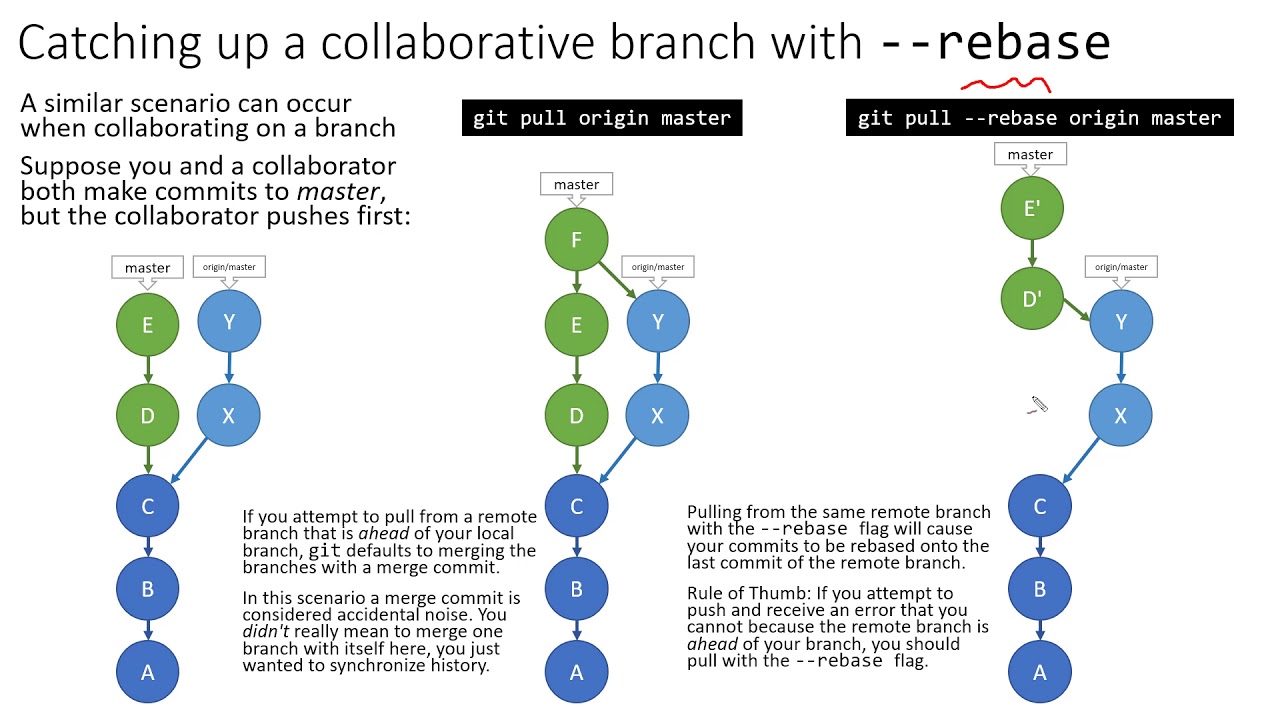
The world of version control systems is pivotal for developers, and understanding how to use Git pull and merge is essential for effective collaboration. In this article, we will delve into the mechanics of Git pull and merge, clarifying what they are, how they work, and why they matter in the software development lifecycle. Git is widely recognized as one of the most powerful tools for managing code changes, making it a crucial skill for developers at any level.
As we explore the intricacies of Git pull and merge, we'll provide practical examples, best practices, and tips to enhance your understanding. Whether you are a beginner wanting to learn the basics or an experienced developer seeking to refine your skills, this guide aims to cater to your needs. By the end, you will be equipped with the knowledge needed to navigate Git with confidence.
Let’s embark on this journey of mastering Git pull and merge, ensuring you are well-prepared to manage your code effectively and collaboratively.
Table of Contents
- What is Git Pull?
- How Git Pull Works
- What is Git Merge?
- How Git Merge Works
- When to Use Pull and Merge
- Best Practices for Git Pull and Merge
- Common Issues and Solutions
- Conclusion
What is Git Pull?
Git pull is a command used in the Git version control system to update your local repository with changes from a remote repository. Essentially, it fetches new data from a remote repository and merges it into your current branch. This command simplifies the process of collaboration by ensuring that your local copy of the project is up-to-date.
Key Features of Git Pull
- Combines two commands:
git fetchandgit merge. - Updates your local branch with changes from the remote branch.
- Helps maintain up-to-date project files across multiple developers.
How Git Pull Works
When you execute the git pull command, Git performs two main actions:
- Fetch: Git retrieves the latest changes from the remote repository. This includes all commits and branches.
- Merge: Git then merges those changes into your current branch. If there are no conflicts, this process happens automatically.
The command can be executed as follows:
git pull origin mainIn this example, origin is the name of the remote repository, and main is the branch you want to pull from.
What is Git Merge?
Git merge is a command that allows you to combine changes from different branches within your local repository. It is an essential part of the collaborative workflow, enabling developers to integrate their features or fixes into the main codebase.
Key Features of Git Merge
- Integrates changes from one branch into another.
- Maintains the history of commits from both branches.
- Supports both fast-forward and non-fast-forward merges.
How Git Merge Works
When you run the git merge command, Git combines the changes from specified branches. If there are no conflicting changes, the merge will complete automatically, creating a new commit that represents the merged state. The basic syntax looks like this:
git merge feature-branchThis command will merge the feature-branch into your current branch.
When to Use Pull and Merge
Understanding when to use Git pull and Git merge is crucial for effective version control. Here are some scenarios:
- Use
git pullwhen you want to update your local branch with the latest changes from the remote repository. - Use
git mergewhen you want to integrate changes from one branch to another within your local repository.
Best Practices for Git Pull and Merge
To ensure a smooth workflow, consider the following best practices:
- Always pull changes before starting new work to avoid conflicts.
- Commit your local changes before pulling or merging to safeguard your work.
- Use descriptive commit messages to clarify the purpose of changes.
Common Issues and Solutions
Developers may encounter various issues while using Git pull and merge. Here are some common problems and suggested solutions:
Merge Conflicts
Merge conflicts occur when changes from two branches overlap. To resolve conflicts:
- Identify the conflicting files using
git status. - Edit the files to resolve the conflicts manually.
- After resolving, stage the changes and commit them.
Detached HEAD State
A detached HEAD state happens when you checkout a commit instead of a branch. To resolve this:
- Create a new branch from your current state using
git checkout -b new-branch. - Commit your changes to the new branch.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding Git pull and merge is vital for effective collaboration in software development. By mastering these commands, you can efficiently manage your codebase and work seamlessly with your team. We encourage you to practice these techniques and share your experiences in the comments below.
For further reading, feel free to explore our other articles on version control and Git best practices. Happy coding!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back here for more insights on software development!
Article Recommendations
- Pioneer Dj
- How Tall Sarah Jessica Parker
- Daryl Hannah
- Digital Strategy_0.xml
- 76 Out Of 80
- Claudine Blanchard Crimes
- Ruben Roman
- Exterior Joint Compound
- How Old Is Adriana Lima 2024
- How Old Is Miguel Diaz