Understanding binary multiplication is essential for anyone interested in computer science and digital electronics. This process is not just a theoretical exercise but a fundamental operation that underpins how computers perform arithmetic calculations. In this article, we will delve deep into the methods of multiplying binary numbers, providing clear explanations, examples, and practical applications to solidify your understanding of this topic.
Binary multiplication operates on the same principles as decimal multiplication but requires a different approach due to the binary number system's unique characteristics. By breaking down the multiplication process step by step, you will gain confidence in performing binary operations, whether manually or using computer algorithms. This guide aims to be a valuable resource for beginners and experienced learners alike.
We will explore various methods of binary multiplication, including the traditional method, the use of bitwise operations, and insights into implementing these techniques in programming. Additionally, we will provide a section dedicated to common pitfalls and how to avoid them, ensuring you have all the tools necessary to master binary multiplication.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Binary Numbers
- Binary Multiplication Methods
- Traditional Binary Multiplication
- Using Bitwise Operations for Multiplication
- Real-World Applications of Binary Multiplication
- Common Pitfalls in Binary Multiplication
- Practice Problems
- Conclusion
Understanding Binary Numbers
Before we dive into multiplication, it's crucial to understand the binary number system. Binary is a base-2 numeral system that uses only two digits: 0 and 1. Each digit in a binary number represents a power of 2, making binary an efficient way to represent data in computing.
Key Characteristics of Binary Numbers
- Each digit is referred to as a bit.
- Binary numbers are read from right to left, similar to decimal numbers.
- The place value of each bit doubles as you move left.
Binary Multiplication Methods
There are several methods to multiply binary numbers, and understanding each method can help you choose the best one for your needs. The two primary methods we will discuss are the traditional method and the method using bitwise operations.
Traditional Binary Multiplication
The traditional method of binary multiplication is similar to decimal multiplication. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step-by-Step Process
- Write the numbers to be multiplied in binary form.
- Multiply each bit of the second number by the entire first number, shifting left for each subsequent bit.
- Add all the resulting binary numbers together.
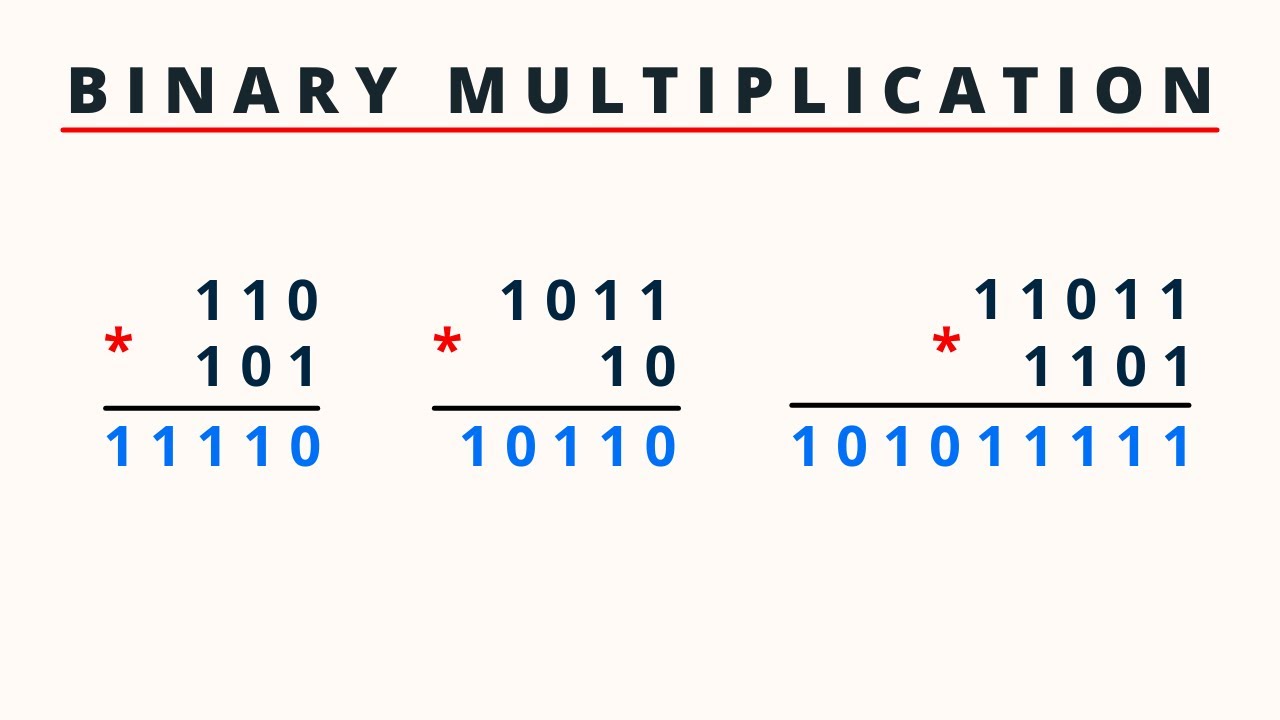
Example: Multiply 1011 (11 in decimal) by 101 (5 in decimal)
Step 1: Write the numbers:
1011 x 101
Step 2: Multiply and shift:
1011 (This is 1011 * 1, no shift) 0000 (This is 1011 * 0, shift one position left) 1011 (This is 1011 * 1, shift two positions left)
Step 3: Add the results:
1011 + 0000 + 101100 --------- 110111
The result is 110111, which is 55 in decimal.
Using Bitwise Operations for Multiplication
Another method to multiply binary numbers is by using bitwise operations. This method is particularly useful in programming and computer algorithms.
Bitwise Shifts and AND Operation
In this method, we use the left shift (<<) and bitwise AND (&) operations:
- Initialize a result variable to 0.
- While the second number is greater than 0:
- If the least significant bit of the second number is 1, add the first number to the result.
- Shift the first number left by one (this is equivalent to multiplying by 2).
- Shift the second number right by one (this is equivalent to dividing by 2).
Real-World Applications of Binary Multiplication
Binary multiplication is widely used in various fields, including:
- Computer Programming: Efficiently implementing mathematical operations in algorithms.
- Data Processing: Manipulating bit-level data in digital electronics.
- Cryptography: Performing complex calculations for secure communications.
Common Pitfalls in Binary Multiplication
While multiplying binary numbers, some common mistakes can occur:
- Misalignment of numbers during addition.
- Incorrect shifting of bits.
- Forgetting to carry over when necessary.
To avoid these pitfalls, practice regularly and double-check your work.
Practice Problems
To solidify your understanding of binary multiplication, try solving these problems:
- Multiply 1101 by 1010.
- Multiply 111 by 11.
- Multiply 1001 by 100.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored the essential topic of binary multiplication, its methods, and real-world applications. Understanding how to multiply binary numbers is not only important for academic purposes but also essential for practical applications in computer science and digital technology.
We encourage you to practice the methods discussed and explore further resources to enhance your skills. If you have questions or comments, feel free to leave them below or share this article with others who may find it helpful!
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you again on our site for more insightful articles!
Article Recommendations
- Deacon Johnson
- Light Therapy
- Poker Face Sunglasses
- Risk Territory Between Ukraine And Siberia Nyt
- Career Advancement_0.xml
- Global Impact_0.xml
- Cost To Extend Garage
- How To Make Raphael In Infinite Craft
- Galaxy Playdough
- Tumblr Fashion Male