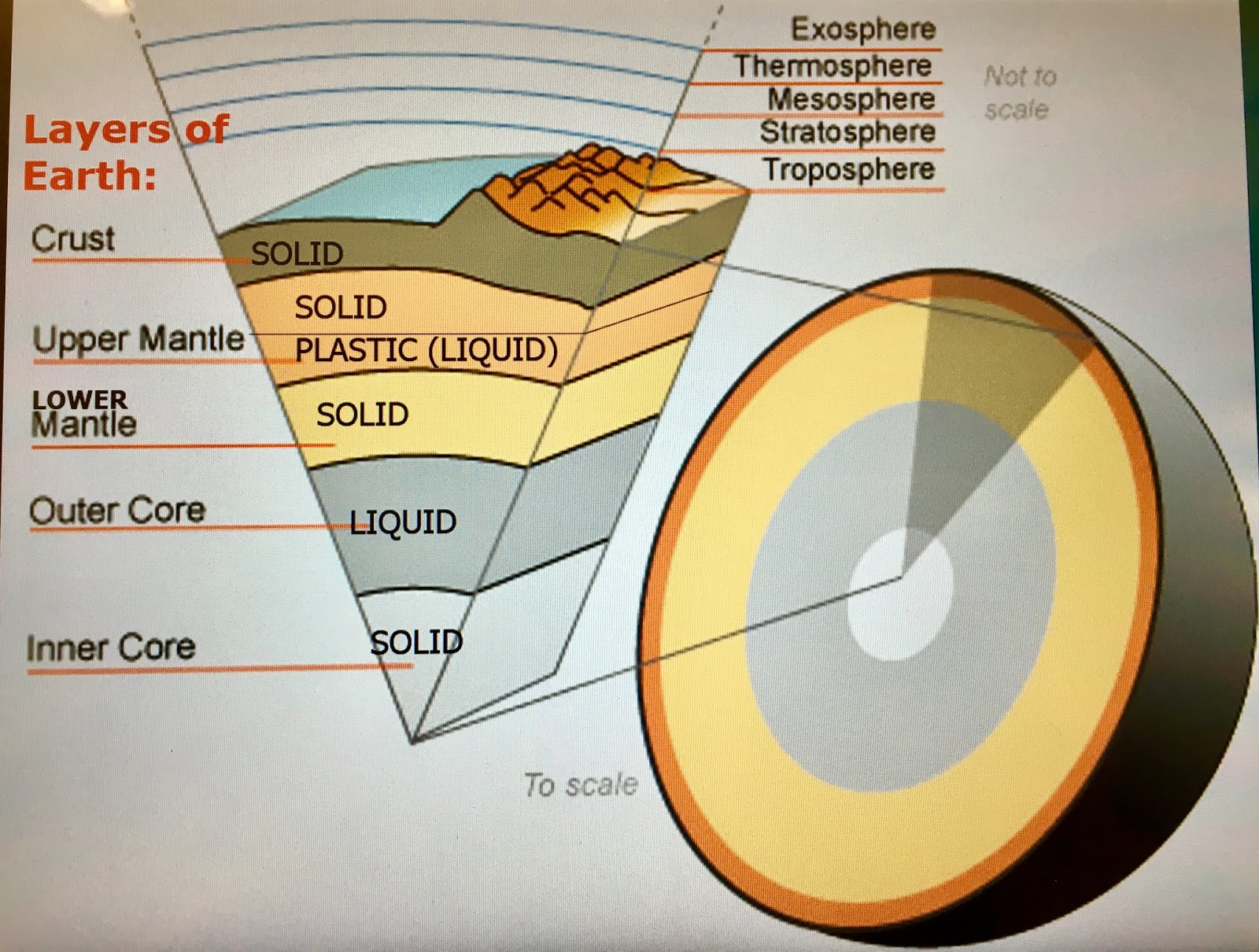
The lithosphere and asthenosphere are crucial components of Earth's structure, playing a vital role in geological processes and the planet's dynamics. These layers not only influence tectonic activity but also affect the environment in which we live. Understanding the differences and interactions between the lithosphere and asthenosphere is essential for anyone interested in geology, geography, or Earth sciences.
This article will delve into the characteristics, composition, and significance of the lithosphere and asthenosphere. We will also explore how these layers interact with each other and their implications for the Earth's geology. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will have a clearer understanding of these two important layers and their roles in shaping our planet.
Whether you are a student, educator, or simply a curious individual, this article aims to provide you with valuable insights into the lithosphere and asthenosphere. So, let’s embark on this informative journey to uncover the mysteries of our planet's layers!
Table of Contents
- 1. What is the Lithosphere?
- 2. The Composition of the Lithosphere
- 3. Characteristics of the Asthenosphere
- 4. Differences Between Lithosphere and Asthenosphere
- 5. The Role of Lithosphere in Plate Tectonics
- 6. The Importance of the Asthenosphere
- 7. Interaction Between Lithosphere and Asthenosphere
- 8. Conclusion and Future Insights
1. What is the Lithosphere?
The lithosphere is defined as the outermost layer of the Earth, encompassing both the crust and the uppermost portion of the mantle. It plays a fundamental role in the geology of our planet and is characterized by its rigidity and mechanical strength. The lithosphere is divided into several tectonic plates, which float on the more pliable asthenosphere beneath it.
Key Features of the Lithosphere
- Rigid and brittle layer
- Thickness varies from 5 km (oceanic lithosphere) to about 70 km (continental lithosphere)
- Composed mainly of silicate rocks
- Includes both continental and oceanic crust
2. The Composition of the Lithosphere
The lithosphere is primarily composed of a variety of rock types, which can be categorized into three main types:
- Igneous Rocks: Formed from the solidification of molten magma. Examples include granite and basalt.
- Sedimentary Rocks: Formed from the accumulation of sediment. Common examples are limestone and sandstone.
- Metamorphic Rocks: Formed from existing rocks that undergo transformation due to heat and pressure. Examples include schist and marble.
3. Characteristics of the Asthenosphere
The asthenosphere lies beneath the lithosphere and is characterized by its semi-fluid nature. This layer allows for the movement of tectonic plates above it, making it essential for the dynamics of plate tectonics.
Key Features of the Asthenosphere
- Partially molten layer of the upper mantle
- Thickness ranges from 100 km to 700 km below the Earth's surface
- Behaves like a viscous fluid over geological time scales
- Facilitates the movement of tectonic plates
4. Differences Between Lithosphere and Asthenosphere
While both the lithosphere and asthenosphere are integral parts of Earth's structure, they have distinct differences:
- Composition: The lithosphere is composed of solid rocks, while the asthenosphere contains partially molten material.
- Physical Properties: The lithosphere is rigid, whereas the asthenosphere is ductile and can flow.
- Thickness: The lithosphere varies in thickness from 5 km to 70 km, while the asthenosphere extends from about 100 km to 700 km deep.
5. The Role of Lithosphere in Plate Tectonics
The lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that float on the asthenosphere. These plates are constantly moving, leading to various geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and mountain building.
Types of Plate Boundaries
- Divergent Boundaries: Plates move apart, creating new crust.
- Convergent Boundaries: Plates collide, leading to subduction or mountain formation.
- Transform Boundaries: Plates slide past one another, causing earthquakes.
6. The Importance of the Asthenosphere
The asthenosphere plays a crucial role in facilitating the movement of tectonic plates. Its semi-fluid nature allows for the convection currents that drive plate tectonics, influencing the Earth's surface and leading to significant geological events.
Implications of Asthenosphere Movement
- Formation of new landforms and landscapes
- Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions
- Sea-floor spreading and continental drift
7. Interaction Between Lithosphere and Asthenosphere
The interaction between the lithosphere and asthenosphere is a dynamic process that shapes the Earth's surface. The lithosphere's rigidity contrasts with the asthenosphere's fluidity, allowing for the movement of tectonic plates and the occurrence of geological events.
Examples of Interaction
- Subduction zones where oceanic lithosphere is forced into the asthenosphere
- Rift zones where the lithosphere is pulled apart, allowing the asthenosphere to rise
- Mountain ranges formed by the collision of continental lithosphere
8. Conclusion and Future Insights
In conclusion, understanding the lithosphere and asthenosphere is essential for grasping the complexities of Earth's geology. These two layers interact continuously, driving the dynamic processes that shape our planet.
As we advance our studies in geology and Earth sciences, it is crucial to continue exploring the intricacies of these layers. We encourage readers to leave comments, share their thoughts, or explore more articles on related topics to further their understanding of Earth's structure.
Thank you for taking the time to read this comprehensive guide on the lithosphere and asthenosphere. We hope you found the information valuable and insightful, and we invite you to return for more engaging content in the future!
Article Recommendations
- Dinosaur Dung
- Career Advancement_0.xml
- Water Softener Overflowing Brine Tank
- Deacon Johnson
- Galaxy Playdough
- Hig Roberts
- Collision Repair Before And After
- Chevy S10 Steering Wheel
- Nikki Minja Naked
- Best True Story Movies