DC generator diagram is an essential topic in electrical engineering, especially for those interested in understanding how direct current generators work. These machines have significant applications in various fields, providing power for everything from small electronic devices to large industrial systems. In this article, we will explore the various components of a DC generator, analyze different types of diagrams, and provide insights into their functionality and applications.
The importance of DC generators cannot be understated, as they have been a cornerstone of electrical power generation since the late 19th century. With the rise of renewable energy and advancements in technology, understanding the working principles of DC generators has become increasingly relevant. This article aims to provide a detailed explanation of the DC generator diagram, including its structure, types, and operational principles.
By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of DC generator diagrams, enabling them to grasp the underlying concepts that govern these essential machines. Whether you are a student, an engineer, or simply someone curious about electrical systems, this guide will offer valuable insights into the world of DC generators.
Table of Contents
- What is a DC Generator?
- Components of a DC Generator
- Types of DC Generators
- DC Generator Diagram Explained
- How a DC Generator Works
- Applications of DC Generators
- Advantages and Disadvantages of DC Generators
- Conclusion
What is a DC Generator?
A DC generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into direct current electrical energy. It operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a conductor moving through a magnetic field generates an electric current. These generators are widely used in various applications, including battery charging, electroplating, and powering small motors.
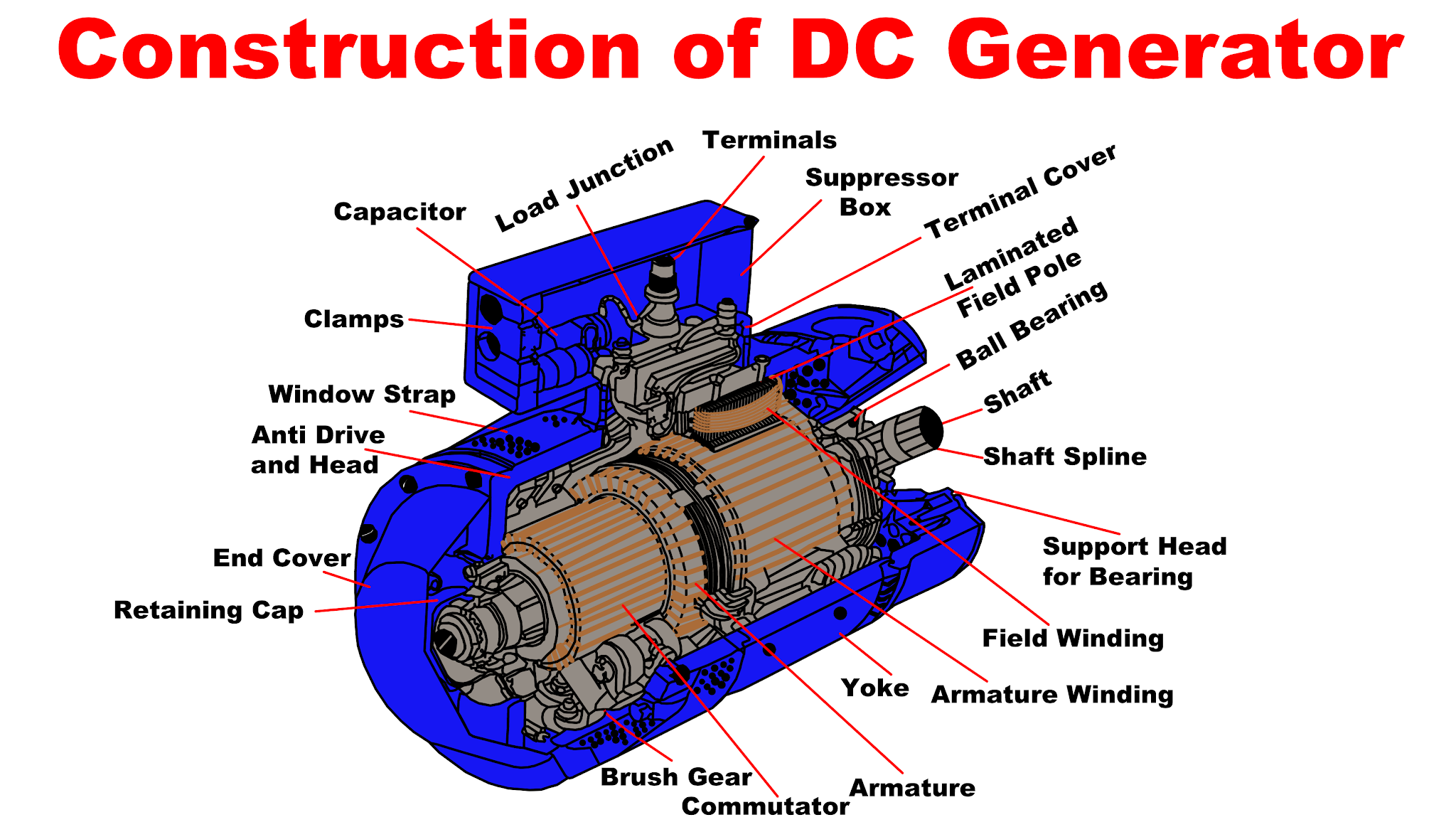
Components of a DC Generator
Understanding the components of a DC generator is crucial for interpreting its diagram. The main components include:
- Stator: The stationary part of the generator that contains the field windings.
- Rotor: The rotating part of the generator that consists of the armature windings.
- Commutator: A mechanical switch that reverses the current direction in the armature windings.
- Brushes: Conductive materials that maintain electrical contact with the rotating commutator.
- Field Windings: Coils of wire that generate a magnetic field when current flows through them.
Types of DC Generators
DC generators can be classified into three main types based on their field connection:
- Series DC Generator: In this type, the field windings are connected in series with the armature. It provides high current output but low voltage.
- Shunt DC Generator: Here, the field windings are connected in parallel with the armature. It produces a stable voltage and is commonly used in various applications.
- Compound DC Generator: This type combines both series and shunt windings. It can be either long compound or short compound, depending on the configuration.
DC Generator Diagram Explained
The DC generator diagram illustrates the relationship between the various components of the generator. A typical diagram includes labels for the stator, rotor, field windings, commutator, and brushes. Understanding this diagram is essential for troubleshooting and designing DC generator systems.
Example of a Basic DC Generator Diagram
Below is a simplified version of a basic DC generator diagram:
- Label each component clearly, such as stator, rotor, and commutator.
- Use arrows to indicate the direction of current flow.
- Show the magnetic field's orientation.
How a DC Generator Works
The operation of a DC generator involves several steps:
- The rotor spins within the magnetic field generated by the stator.
- As the rotor turns, the armature windings cut through the magnetic lines of force, inducing an electromotive force (EMF).
- The commutator converts the alternating current (AC) generated in the armature windings into direct current (DC).
- Brushes maintain contact with the commutator, allowing the generated current to flow to the external circuit.
Applications of DC Generators
DC generators have a wide range of applications, including:
- Battery charging for electric vehicles and backup power systems.
- Powering small motors used in tools and appliances.
- Electroplating processes in manufacturing.
- Providing emergency power in critical systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DC Generators
Advantages
- Simple construction and easy maintenance.
- Can provide high current output when needed.
- Stable voltage output in shunt and compound configurations.
Disadvantages
- Lower efficiency compared to AC generators.
- Requires regular maintenance due to brush wear.
- Limited applications in modern electrical systems.
Conclusion
In summary, the DC generator diagram is a vital tool for understanding how these machines operate. By exploring the components, types, and functionality of DC generators, we have gained insights into their applications and importance in various fields. As technology continues to evolve, knowledge of DC generators remains relevant for engineers and enthusiasts alike.
We encourage readers to leave comments, share this article, or explore more related content on our site to deepen their understanding of DC generators and electrical systems.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to welcoming you back for more informative articles on electrical engineering topics!
Article Recommendations
- Kylie Jenner Before Surgery
- Ella Bleu S Career Updates
- Mary Anne Macleod Trump
- Risk Territory Between Ukraine And Siberia Nyt
- Lax Plane Spotting Locations
- Collision Repair Before And After
- Jennifer Syme Crash
- Streaming Device Whose Name Means Six
- Hig Roberts
- Clothes Not Smelling Fresh After Washing