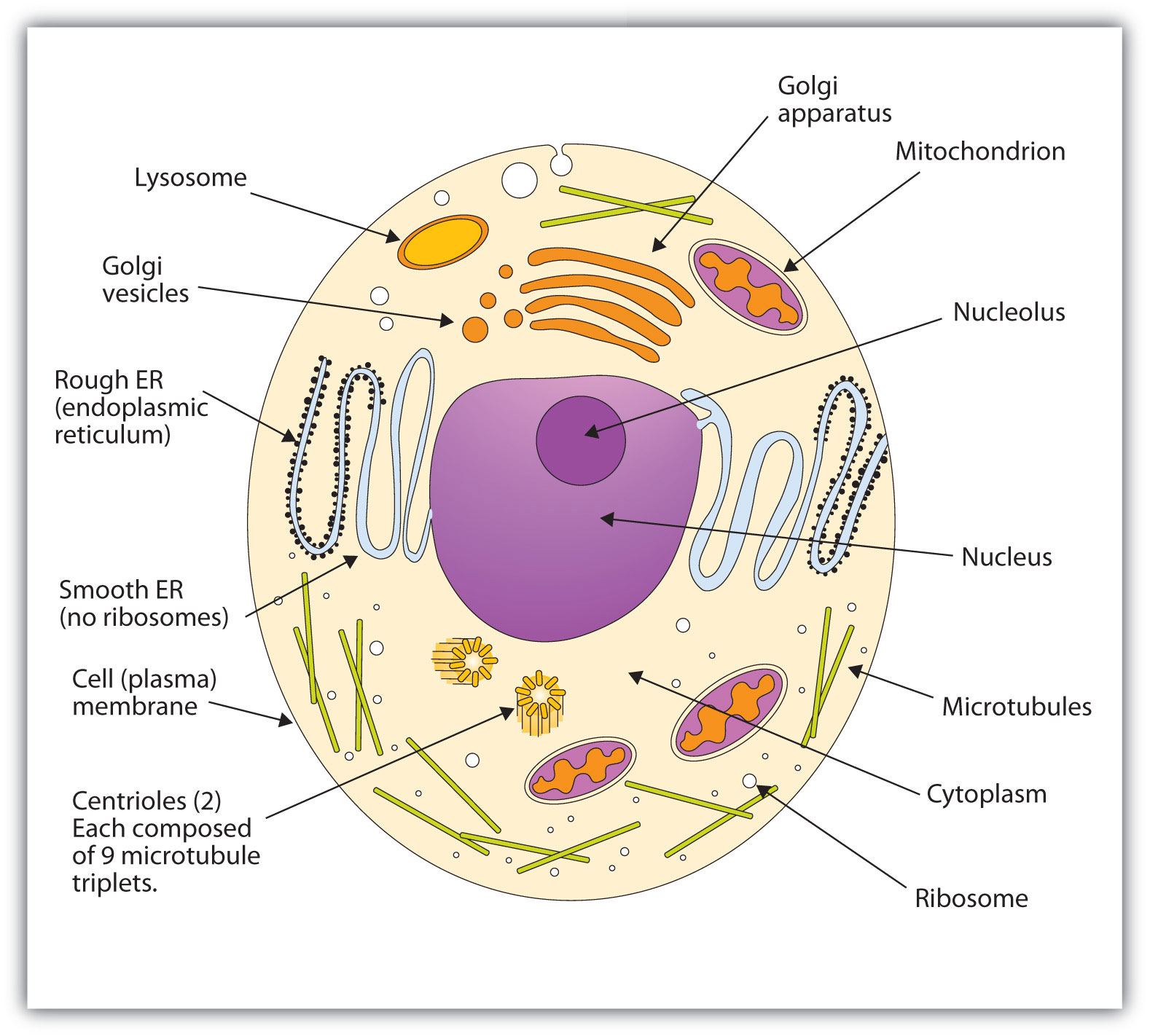
The diagram of an animal cell is essential for anyone looking to understand the fundamental unit of life. Animal cells are the building blocks of all animals, and they play a crucial role in the functioning of living organisms. In this article, we will delve into the structure, functions, and significance of animal cells, providing you with a detailed overview that is both informative and engaging.
Cells are often referred to as the "basic unit of life," and understanding their structure is paramount for students, educators, and anyone interested in biology. The animal cell diagram serves as a visual representation that helps in recognizing various organelles and their functions. This guide aims to provide a thorough analysis of the animal cell, ensuring you have all the information needed to grasp the intricacies of cellular biology.
Throughout this article, we will explore the different components of an animal cell, their functions, and how they work together to sustain life. Whether you are a student preparing for exams or simply curious about biology, this article will serve as a valuable resource. Let’s dive into the world of animal cells!
Table of Contents
- 1. What is an Animal Cell?
- 2. Key Components of an Animal Cell
- 3. Functions of the Organelles
- 4. The Importance of Animal Cells in Biology
- 5. Differences Between Animal and Plant Cells
- 6. How Animal Cells Reproduce
- 7. Visualizing Animal Cells: The Diagram
- 8. Conclusion and Further Reading
1. What is an Animal Cell?
An animal cell is a type of eukaryotic cell that is distinct from prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria. Eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Animal cells are typically smaller than plant cells and lack certain structures such as cell walls and chloroplasts.
Animal cells are versatile and can perform various functions, depending on their type and location in the body. They form tissues, organs, and systems, enabling the body to function effectively.
2. Key Components of an Animal Cell
The structure of an animal cell is composed of several key components, each playing a specific role. Below is a list of the main organelles found in animal cells:
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Cell Membrane
- Mitochondria
- Ribosomes
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth and Rough)
- Golgi Apparatus
- Lysosomes
- Centrioles
Data Table of Animal Cell Organelles
| Organelle | Function |
|---|---|
| Nucleus | Stores genetic information and controls cell activities. |
| Cytoplasm | Medium for biochemical reactions and organelle placement. |
| Cell Membrane | Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. |
| Mitochondria | Produces energy (ATP) through respiration. |
| Ribosomes | Synthesizes proteins. |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Processes and transports proteins and lipids. |
| Golgi Apparatus | Modifies and packages proteins for secretion. |
| Lysosomes | Digestive organelles that break down waste. |
| Centrioles | Involved in cell division. |
3. Functions of the Organelles
Each organelle within the animal cell has a unique function that contributes to the cell's overall operation. Here’s a more detailed look at the functions of the major organelles:
Nucleus
The nucleus is often referred to as the control center of the cell. It contains the cell's DNA, which holds the instructions for making proteins and other important molecules. The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear envelope that protects the genetic material.
Mitochondria
Commonly known as the powerhouse of the cell, mitochondria are responsible for producing ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the energy currency of the cell. They perform cellular respiration, converting nutrients into energy.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are the protein synthesis sites. They can be found floating freely in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Ribosomes translate the genetic code from mRNA to build proteins.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are the digestive system of the cell, containing enzymes that break down waste materials and cellular debris. They play a critical role in recycling cellular components and maintaining cellular health.
4. The Importance of Animal Cells in Biology
Understanding animal cells is fundamental in numerous fields of study, including genetics, medicine, and biotechnology. Here are some reasons why animal cells are significant:
- Research in genetics and disease: Animal cells help researchers study genetic disorders and develop treatments.
- Biotechnology applications: Animal cells are used in vaccine production and drug development.
- Understanding cellular processes: Insights into cellular functions lead to advancements in health and medicine.
5. Differences Between Animal and Plant Cells
While animal cells share many similarities with plant cells, there are key differences that set them apart:
- Cell Wall: Plant cells have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose, while animal cells do not.
- Chloroplasts: Plant cells contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis; animal cells do not.
- Shape: Animal cells are typically round or irregular in shape, while plant cells are more rectangular.
- Vacuoles: Plant cells have large central vacuoles for storage, whereas animal cells have smaller vacuoles.
6. How Animal Cells Reproduce
Animal cells reproduce primarily through a process called mitosis, which ensures that when a cell divides, each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes. The stages of mitosis include:
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
7. Visualizing Animal Cells: The Diagram
The diagram of an animal cell is a powerful tool for visualizing its structure and functions. It typically includes labeled parts, allowing for easy identification of organelles. Here are some essential elements that are often included in an animal cell diagram:
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Cell Membrane
- Mitochondria
- Ribosomes
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Golgi Apparatus
- Lysosomes
8. Conclusion and Further Reading
In conclusion, the diagram of an animal cell provides invaluable insights into the structure and function of this fundamental unit of life. By understanding the various organelles and their roles, we can appreciate the complexity and efficiency of living organisms. If you're interested in deepening your understanding of biology, consider exploring additional resources or textbooks that cover cellular biology extensively.
We invite you to leave a comment below, share this article with friends, or explore other articles on our site for more information on biological topics.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you again soon!
Article Recommendations
- Clr Soak Overnight
- Ruben Roman
- Nikki Minja Naked
- How Old Is Miguel Diaz
- Personal Wifi
- Travis Kelce August 2024
- Mario Lopez
- Collision Repair Before And After
- Light Therapy
- Kamila Valieva