Cellular respiration is a fundamental biological process that provides energy for all living organisms. Understanding the four steps of cellular respiration is essential for grasping how cells convert nutrients into usable energy. In this article, we will explore each step in detail, providing a thorough understanding of how cellular respiration supports life. Whether you are a student, educator, or simply curious about biology, this guide will provide valuable insights into this vital process.
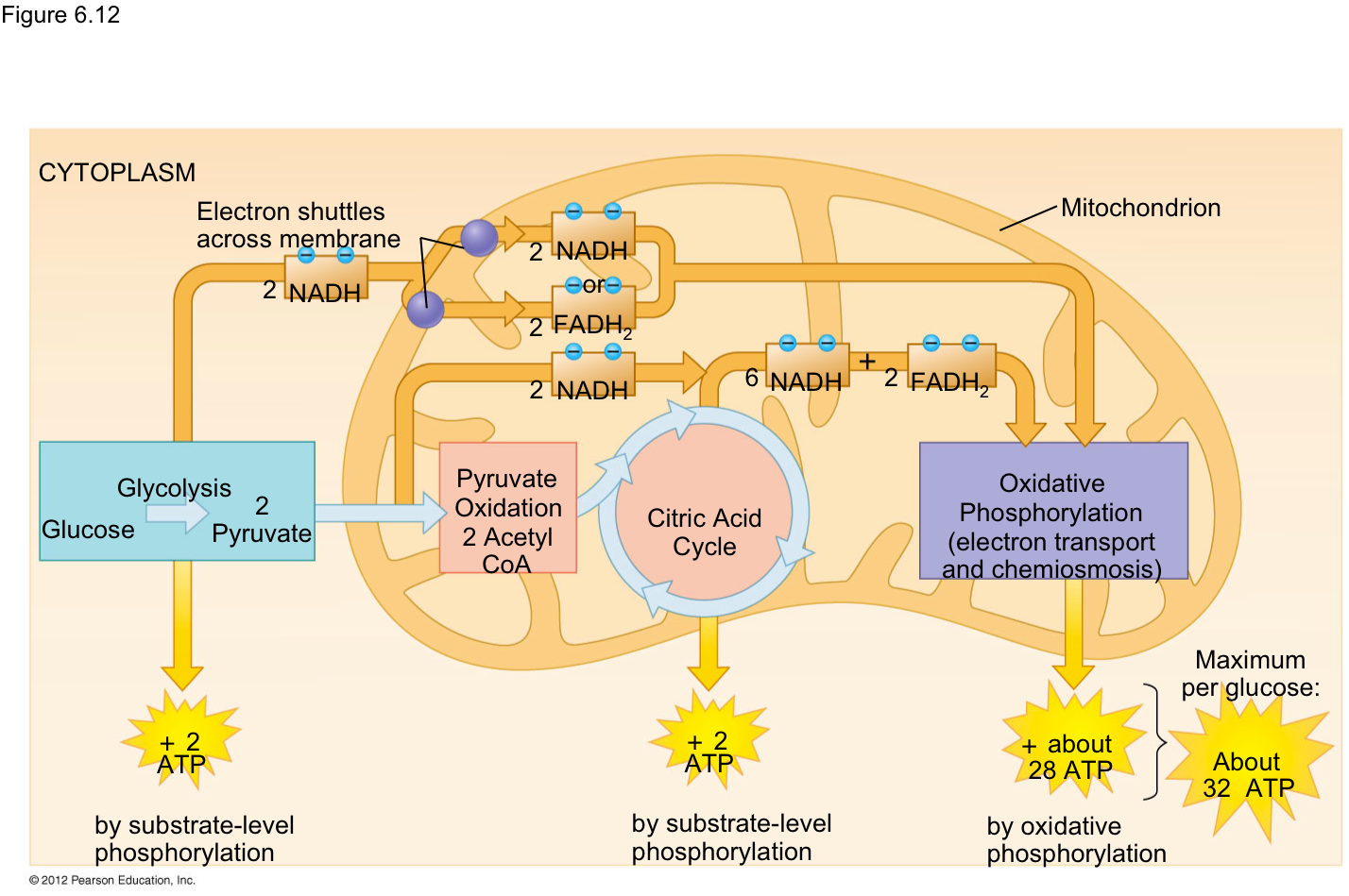
In the world of biology, cellular respiration is a critical function that allows organisms to harness energy from food. This process not only fuels cellular activities but also plays a crucial role in maintaining life. The four steps of cellular respiration include Glycolysis, the Krebs Cycle, the Electron Transport Chain, and Oxidative Phosphorylation. Each of these steps is intricately connected, working together to ensure that energy is efficiently produced and utilized.
This article aims to provide an in-depth look at these four steps, the biochemical processes involved, and their significance in the context of cellular metabolism. We will also discuss the importance of understanding cellular respiration for various applications in health, medicine, and environmental science. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of cellular respiration and uncover the secrets behind the energy production that sustains life.
Table of Contents
- 1. Glycolysis
- 2. The Krebs Cycle
- 3. The Electron Transport Chain
- 4. Oxidative Phosphorylation
- 5. Importance of Cellular Respiration
- 6. Conclusion
- 7. References
1. Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first step in the process of cellular respiration, occurring in the cytoplasm of cells. This anaerobic process begins with a glucose molecule and ends with the production of pyruvate, ATP, and NADH. Here’s a breakdown of what happens during glycolysis:
- **Glucose Activation:** The glucose molecule is phosphorylated using ATP, which helps to trap the glucose inside the cell.
- **Cleavage Phase:** The six-carbon sugar is split into two three-carbon molecules called glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P).
- **Energy Harvesting:** G3P is further processed to produce ATP and NADH, which are crucial energy carriers.
Overall, glycolysis produces a net gain of 2 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules, setting the stage for the next steps in cellular respiration.
2. The Krebs Cycle
Also known as the Citric Acid Cycle or TCA Cycle, the Krebs Cycle takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. This cycle is aerobic and requires oxygen to proceed. Here’s how the Krebs Cycle works:
- **Acetyl-CoA Formation:** Pyruvate produced during glycolysis is converted into Acetyl-CoA, which enters the Krebs Cycle.
- **Cycle Initiation:** Acetyl-CoA combines with oxaloacetate to form citric acid, which undergoes a series of transformations.
- **Energy Production:** Throughout the cycle, NADH and FADH2 are generated, along with ATP and carbon dioxide as byproducts.
The Krebs Cycle is crucial for the production of high-energy electron carriers, which are essential for the next step of cellular respiration.
3. The Electron Transport Chain
The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) is the final stage of cellular respiration and occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane. This step is pivotal for ATP production. Here’s how it works:
- **Electron Transfer:** NADH and FADH2 donate electrons to the ETC, where they are passed along a series of proteins.
- **Proton Gradient Creation:** As electrons move through the chain, protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space, creating a proton gradient.
- **ATP Synthesis:** The flow of protons back into the matrix through ATP synthase generates ATP.
This stage is responsible for the majority of ATP produced during cellular respiration, with up to 34 ATP molecules generated from one glucose molecule.
4. Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation encompasses the final steps of the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis. Here’s a closer look:
- **Oxygen as the Final Electron Acceptor:** Oxygen combines with electrons and protons to form water, a crucial step for maintaining the flow of electrons.
- **ATP Yield:** The majority of ATP produced during cellular respiration occurs here, making it the most efficient energy-generating process.
This process highlights the importance of oxygen in cellular respiration and its role as a vital component for energy production.
5. Importance of Cellular Respiration
Understanding the four steps of cellular respiration is essential for various fields, including medicine, environmental science, and energy production. Here are some key points highlighting its significance:
- **Energy Production:** Cellular respiration is the primary source of ATP, which is essential for cellular functions.
- **Metabolism Regulation:** It plays a crucial role in regulating metabolic pathways and maintaining homeostasis.
- **Health Implications:** Understanding cellular respiration can lead to insights into metabolic diseases, obesity, and diabetes.
- **Environmental Impact:** Knowledge of cellular respiration contributes to understanding ecological systems and energy flow.
6. Conclusion
In summary, the four steps of cellular respiration—Glycolysis, the Krebs Cycle, the Electron Transport Chain, and Oxidative Phosphorylation—play a vital role in energy production for all living organisms. Each step is intricately linked, ensuring that cells can efficiently convert nutrients into usable energy. By understanding these processes, we gain valuable insights into biology, health, and the environment.
We encourage you to leave your thoughts in the comments below, share this article with others, or explore more of our content to deepen your understanding of cellular processes.
7. References
- Campbell, N. A., & Reece, J. B. (2005). Biology. Pearson.
- Alberts, B. et al. (2014). Molecular Biology of the Cell. Garland Science.
- Nelson, D. L., & Cox, M. M. (2017). Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. W.H. Freeman.
Article Recommendations
- Mario Lopez
- How Tall Sarah Jessica Parker
- Jennifer Syme Crash
- Streaming Device Whose Name Means Six
- Digital Revolution_0.xml
- Legal Seafood Recipes Crab Cakes
- How Did Jennifer Syme Pass Away
- Brand Building_0.xml
- Tumblr Fashion Male
- Piper Parabo