Understanding the intricacies of data analysis is crucial in today's data-driven world. One of the key functionalities offered by SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) is the ability to create frequency tables, which are essential for summarizing categorical data. Whether you are a researcher, student, or data analyst, mastering the SPSS frequency table will provide you with the tools necessary to interpret your data effectively. This article will delve into the significance of frequency tables in SPSS, guiding you through their creation and interpretation.
Frequency tables serve as a foundational element in data analysis, allowing users to observe the distribution and pattern of responses within a dataset. By visualizing how often each category appears, analysts can gain insights into trends and outliers that may require further investigation. The ability to create these tables using SPSS not only streamlines the data analysis process but also enhances the clarity of presented findings.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various aspects of the SPSS frequency table, addressing common questions and concerns that users may encounter. From basic definitions to advanced applications, we aim to equip you with the knowledge needed to utilize SPSS frequency tables to their fullest potential. Let’s embark on this journey to unlock the power of your data!
What is an SPSS Frequency Table?
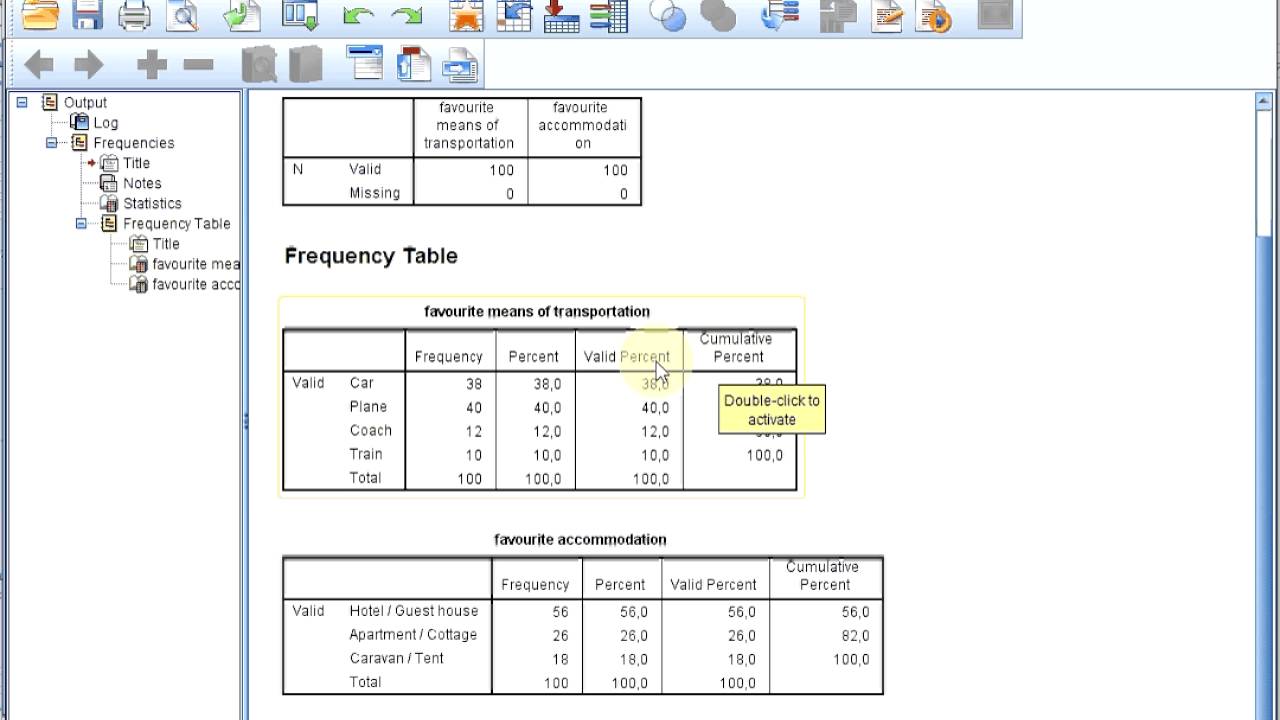
An SPSS frequency table is a statistical tool used to display the number of occurrences of each unique value in a dataset. This is particularly useful when working with categorical data, as it allows researchers to quickly assess how responses are distributed across different categories. The frequency table typically includes the following elements:
- Categories: The distinct values or groups in the dataset.
- Frequency Count: The number of times each category appears in the dataset.
- Percentage: The proportion of each category relative to the total number of observations.
How Do You Create a Frequency Table in SPSS?
Creating a frequency table in SPSS is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to generate your frequency table:
- Open your dataset in SPSS.
- Select the “Analyze” menu.
- Click on “Descriptive Statistics,” then select “Frequencies.”
- Choose the variable(s) for which you want to create the frequency table and move them to the right box.
- Optional: Click on “Statistics” to select additional descriptive measures (e.g., mean, median).
- Click “OK” to generate the frequency table.
What Information Does an SPSS Frequency Table Provide?
The SPSS frequency table provides a wealth of information that can be essential for data analysis:
- Distribution of Responses: It helps in understanding how data is distributed across categories.
- Identifying Trends: Analysts can identify patterns or trends in the data.
- Spotting Outliers: The frequency table can flag any unusual responses that may require further investigation.
What Are the Advantages of Using Frequency Tables?
Frequency tables offer several benefits that contribute to effective data analysis:
- Simplicity: They present data in an easy-to-read format, making it accessible for all stakeholders.
- Clarity: Frequency tables help clarify data distributions, which can be beneficial for presentations and reports.
- Foundation for Further Analysis: They provide a basis for more complex statistical analyses.
How Can You Interpret an SPSS Frequency Table?
Interpreting an SPSS frequency table involves understanding the displayed data:
- Examine the frequency counts to see which categories have the highest and lowest occurrences.
- Look at the percentage column to assess the relative importance of each category.
- Identify any outliers or unexpected results that may indicate data entry errors or unique trends.
Are There Limitations to SPSS Frequency Tables?
While SPSS frequency tables are incredibly useful, they do have some limitations:
- Not Suitable for Continuous Data: Frequency tables are primarily designed for categorical data.
- Loss of Detail: When summarizing data, some detailed information may be lost.
- Potential for Misinterpretation: Without proper context, frequency tables can be misleading.
What Are Some Best Practices for Using SPSS Frequency Tables?
To maximize the effectiveness of your SPSS frequency tables, consider the following best practices:
- Label Your Variables: Clear labeling helps in understanding the context of the data.
- Use Graphical Representations: Complement frequency tables with charts or graphs for visual clarity.
- Review Data Quality: Before creating frequency tables, ensure that your data is clean and free from errors.
Conclusion: Why Mastering the SPSS Frequency Table Matters?
In conclusion, mastering the SPSS frequency table is a vital skill for anyone involved in data analysis. By understanding how to create, interpret, and effectively utilize frequency tables, analysts can gain deeper insights into their data, identify trends, and make informed decisions. As you continue your journey in data analysis, let the SPSS frequency table be a tool that enhances your analytical capabilities and empowers you to present your findings with confidence.
Article Recommendations
- Corinne Foxx
- Light Therapy
- Clr Soak Overnight
- Lola Consuelos Weight Loss Ozempic
- Efficient Strategies_0.xml
- Girl Meets World Cast
- Michael Jordan Tequila Reposado
- Financial Empowerment_0.xml
- Deacon Johnson
- Outdoor Propane Heater Table Top