Gravitational lensing is a fascinating phenomenon that plays a crucial role in our understanding of dark matter and the universe. This effect occurs when a massive object, such as a galaxy or cluster of galaxies, bends the light from objects behind it. The study of gravitational lensing not only provides insights into the distribution of dark matter but also enhances our comprehension of the universe's structure and evolution. In this article, we will explore the intricate relationship between gravitational lensing and dark matter, delving into the science, implications, and current research in the field.
As astronomers and physicists continue to unravel the mysteries of the universe, gravitational lensing has emerged as a key tool for probing dark matter. By observing how light is distorted around massive objects, scientists can infer the presence and distribution of dark matter, which does not emit light and is invisible to traditional observational techniques. Understanding this relationship is paramount, as dark matter constitutes a significant portion of the universe's mass and influences its overall dynamics.
This article will cover various aspects of gravitational lensing, including its types, mechanisms, and the critical role it plays in dark matter research. By the end, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how gravitational lensing helps illuminate the dark matter enigma and shapes our view of the cosmos.
Table of Contents
- What is Gravitational Lensing?
- Types of Gravitational Lensing
- How Does Gravitational Lensing Work?
- The Role of Dark Matter in Gravitational Lensing
- Observational Evidence of Dark Matter through Gravitational Lensing
- Gravitational Lensing in Astrophysics
- Current Research and Future Prospects
- Conclusion
What is Gravitational Lensing?
Gravitational lensing is a phenomenon predicted by Albert Einstein's General Theory of Relativity. It occurs when a massive object, like a galaxy or galaxy cluster, lies between a distant light source and an observer. The gravitational field of the foreground object warps the space around it, causing the light from the background source to bend. This bending effect can result in multiple images of the same background object, magnification of its brightness, or even the formation of arcs and rings around the lensing object.
Key Characteristics of Gravitational Lensing
- Deflection of Light: The core principle of gravitational lensing is the deflection of light by gravity.
- Multiple Images: In some cases, the same distant object can appear in multiple locations due to lensing.
- Magnification: The brightness of distant objects can be amplified, allowing astronomers to study fainter galaxies.
Types of Gravitational Lensing
Gravitational lensing can be classified into three main types: strong lensing, weak lensing, and micro-lensing. Each type has distinct characteristics and implications for dark matter research.
1. Strong Lensing
Strong lensing occurs when the alignment between the lensing object, the background source, and the observer is nearly perfect. This results in dramatic distortions, such as multiple images or Einstein rings. Strong lensing is particularly useful for studying the mass distribution of lensing galaxies and clusters, providing insights into the presence of dark matter.
2. Weak Lensing
Weak lensing involves less precise alignments, leading to subtle distortions in the shapes of background galaxies. Although the effects are more challenging to detect, weak lensing surveys can cover larger areas of the sky, allowing researchers to map the distribution of dark matter across vast cosmic scales.
3. Micro-Lensing
Micro-lensing refers to the temporary increase in brightness of a background star when a smaller mass, such as a planet or a star, passes in front of it. This phenomenon is utilized in the search for exoplanets and studying dark matter in the form of compact objects.
How Does Gravitational Lensing Work?
The mechanics of gravitational lensing can be understood through a few key concepts from general relativity and astrophysics. The bending of light is a result of the curvature of spacetime caused by mass. When light travels near a massive object, its path is altered, leading to the lensing effect.
The Einstein Ring
One of the most striking manifestations of gravitational lensing is the formation of an Einstein ring. This occurs when the source, lens, and observer are perfectly aligned. The light from the background source is bent into a ring-like structure surrounding the lensing mass. Einstein rings serve as powerful tools for measuring the mass of lensing objects and estimating the amount of dark matter present.
Mathematical Framework
The mathematics of gravitational lensing involves several equations that describe how light is deflected by mass. The most significant of these is the lens equation, which relates the positions of the source, lens, and images. By analyzing these equations, scientists can extract information about the mass distribution of the lensing object and the characteristics of dark matter.
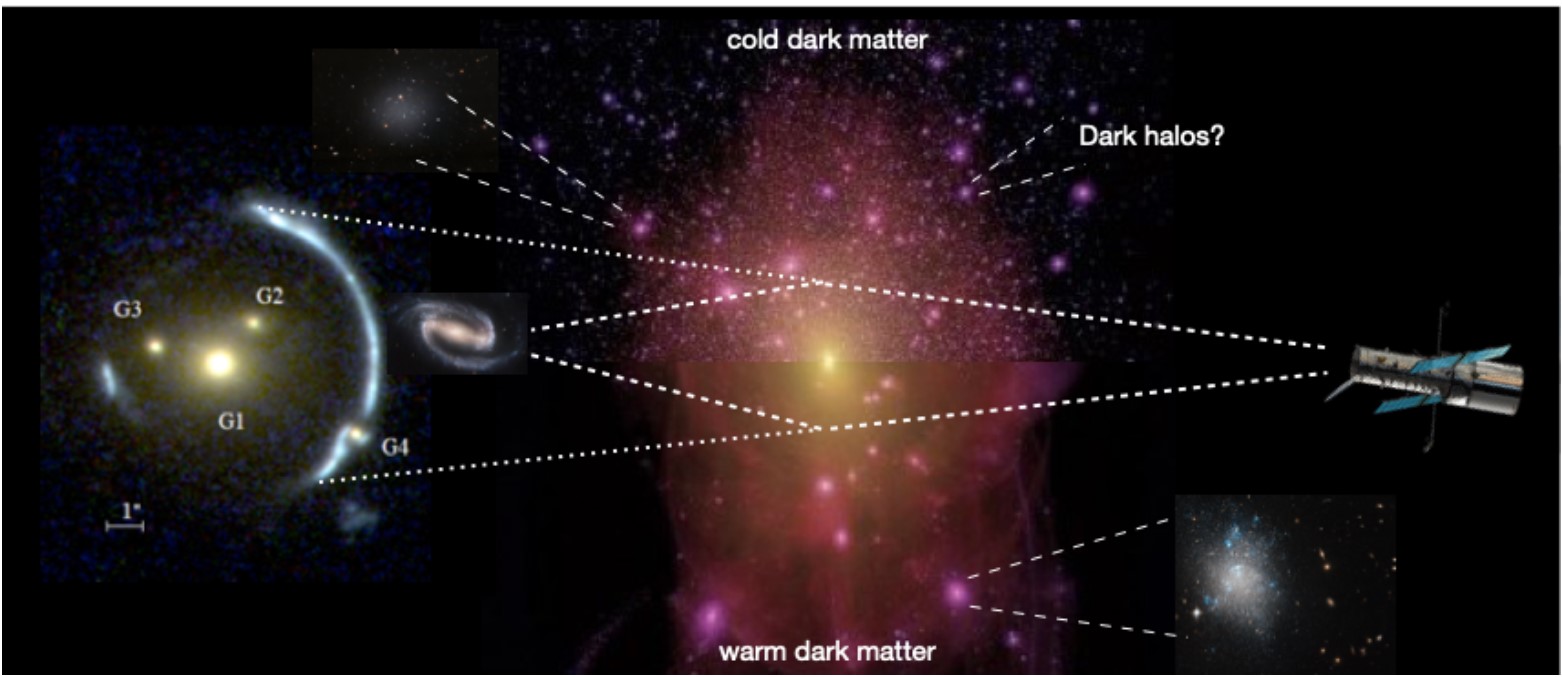
The Role of Dark Matter in Gravitational Lensing
Dark matter, an elusive and non-luminous form of matter, comprises a substantial portion of the universe's total mass. Although it cannot be observed directly, its presence is inferred through gravitational effects on visible matter, including galaxies and galaxy clusters.
Understanding Dark Matter through Lensing
Gravitational lensing serves as a crucial tool for studying dark matter. By observing lensing effects, astronomers can map the distribution of dark matter in galaxy clusters and large-scale structures. The way light is bent provides insights into the mass and spatial distribution of dark matter, helping to refine models of cosmic structure formation.
Dark Matter Profiles
Different models of dark matter propose various density profiles that describe how dark matter is distributed within galaxies and clusters. Gravitational lensing data allows scientists to test these models and determine the most accurate representations of dark matter's behavior in the universe.
Observational Evidence of Dark Matter through Gravitational Lensing
Numerous observational campaigns have utilized gravitational lensing to gather evidence for dark matter's existence and distribution. Some notable examples include:
- Galaxy Clusters: Studies of galaxy clusters, such as the Bullet Cluster, have provided compelling evidence for dark matter. The lensing maps created from these observations reveal that the majority of the mass in these clusters is not associated with the visible galaxies.
- Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB): Gravitational lensing of the CMB offers insights into the distribution of dark matter across the universe's largest scales, helping to validate cosmological models.
- LSST (Large Synoptic Survey Telescope): Future surveys like LSST aim to map the dark matter distribution across the sky using both strong and weak lensing techniques, providing unprecedented data for dark matter research.
Gravitational Lensing in Astrophysics
Gravitational lensing has far-reaching implications beyond dark matter research. It plays a vital role in various astrophysical studies, including:
1. Galaxy Formation and Evolution
By examining how light is distorted by gravitational lensing, astronomers can infer the properties of distant galaxies and their formation history, helping to understand the evolution of the universe.
2. Testing General Relativity
Gravitational lensing offers an opportunity to test Einstein's General Theory of Relativity. Observations of lensing effects can validate or challenge our understanding of gravity and spacetime.
3. Probing the Nature of Dark Energy
In addition to dark matter, gravitational lensing can provide insights into dark energy, the mysterious force driving the universe's accelerated expansion. By examining how lensing varies with cosmic distance, researchers can probe the effects of dark energy on the universe's structure.
Current Research and Future Prospects
The field of gravitational lensing and dark matter research is rapidly evolving, with numerous ongoing projects and future missions aimed at enhancing our understanding of
Article Recommendations
- Japanese Watch Brands
- Wallet With Pull Tab
- Cast Of Hidden Figures
- Best True Story Movies
- Mario Lopez
- Healthy Habits_0.xml
- Travis Kelce August 2024
- Debutante
- Outdoor Propane Heater Table Top
- Tumblr Fashion Male