Molar heat capacity is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics that plays a crucial role in understanding how substances absorb and transfer heat. This property is particularly important in various scientific fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering. In this article, we will delve deep into the definition, significance, and applications of molar heat capacity, helping you grasp its importance in both theoretical and practical scenarios.
In the following sections, we will explore the various aspects of molar heat capacity, including its calculation, types, factors affecting it, and real-world applications. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of molar heat capacity and its significance in both academic and practical contexts.
Table of Contents
- Definition of Molar Heat Capacity
- Formula for Molar Heat Capacity
- Types of Molar Heat Capacity
- Factors Affecting Molar Heat Capacity
- Calculating Molar Heat Capacity
- Applications of Molar Heat Capacity
- Examples of Molar Heat Capacity
- Conclusion
Definition of Molar Heat Capacity
Molar heat capacity is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of a substance by one degree Celsius (°C) or one Kelvin (K). This property indicates how much heat a substance can store and helps in understanding its thermal characteristics. The molar heat capacity can vary significantly between different substances, making it an essential parameter in thermodynamic calculations.
Formula for Molar Heat Capacity
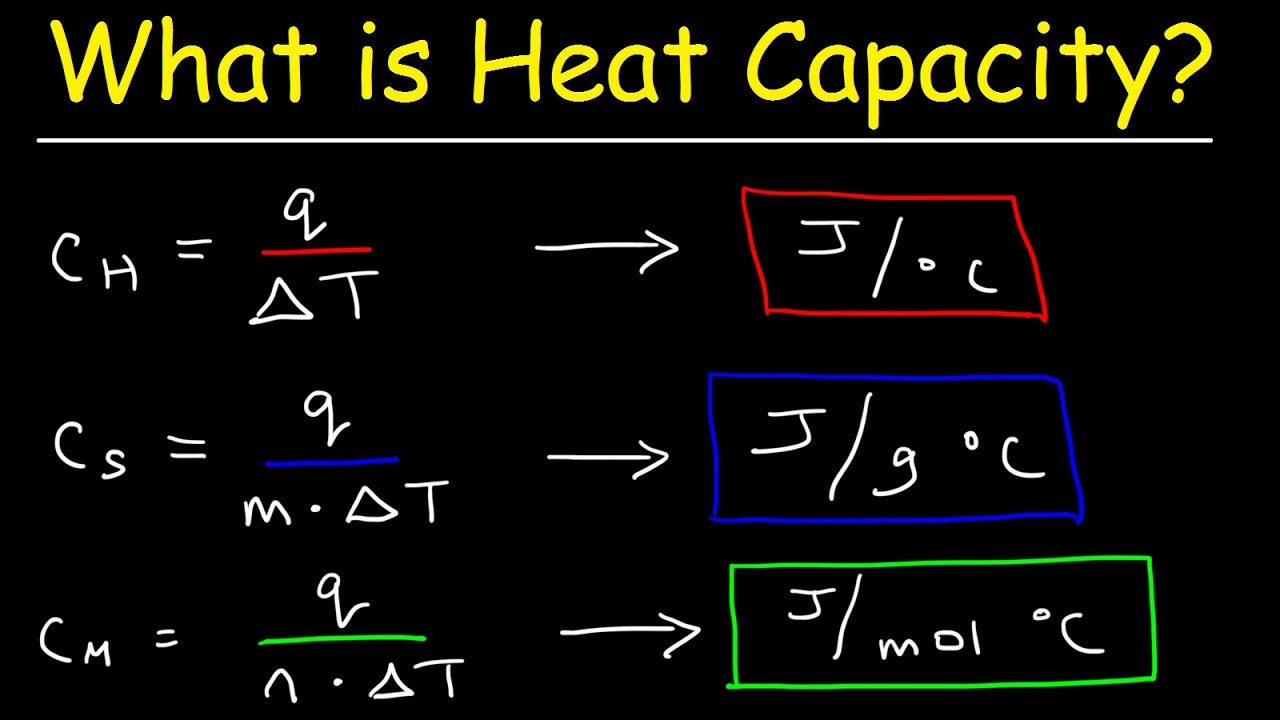
The molar heat capacity (Cm) can be represented mathematically by the following formula:
Cm = Q / (n × ΔT)
Where:
- Q = heat absorbed or released (in joules)
- n = number of moles of the substance
- ΔT = change in temperature (in °C or K)
Types of Molar Heat Capacity
Molar heat capacity can be categorized into two main types based on the conditions under which it is measured:
- Molar Heat Capacity at Constant Volume (Cv): This type measures the heat capacity of a substance when the volume remains constant. It is particularly relevant for gases.
- Molar Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure (Cp): This type measures the heat capacity of a substance when the pressure remains constant. It is commonly used in most practical applications.
Factors Affecting Molar Heat Capacity
Several factors can influence the molar heat capacity of a substance:
- Nature of the Substance: Different materials have varying molecular structures and bonding, which can affect their heat capacity.
- Temperature: The molar heat capacity can change with temperature due to alterations in molecular motion and interactions.
- Phase of the Substance: Molar heat capacity can differ significantly between solids, liquids, and gases.
Calculating Molar Heat Capacity
To calculate the molar heat capacity, follow these steps:
- Measure the amount of heat (Q) transferred to or from the substance.
- Determine the number of moles (n) of the substance involved.
- Calculate the change in temperature (ΔT).
- Use the formula Cm = Q / (n × ΔT) to find the molar heat capacity.
Applications of Molar Heat Capacity
Molar heat capacity has numerous applications across various fields:
- Engineering: Understanding heat capacity is crucial in designing engines, HVAC systems, and chemical reactors.
- Chemistry: Molar heat capacity helps predict reaction behavior and energy changes during reactions.
- Environmental Science: It plays a role in understanding temperature changes in natural systems and climate modeling.
Examples of Molar Heat Capacity
Here are some examples of molar heat capacities for common substances:
| Substance | Cp (J/mol·K) | Cv (J/mol·K) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 75.3 | 75.3 |
| Air | 29.19 | 20.79 |
| Carbon Dioxide | 37.11 | 28.77 |
Conclusion
Molar heat capacity is a vital concept in thermodynamics that helps us understand how substances behave under heat transfer. By knowing the molar heat capacity, scientists and engineers can make informed decisions in various applications, from designing engines to predicting chemical reactions. We encourage you to explore more about this topic and share your thoughts in the comments below!
For further reading, consider checking out additional articles on thermodynamics and heat transfer principles. Stay curious and keep learning!
Article Recommendations
- Lola Consuelos Weight Loss Ozempic
- Three Cornered Hat Crossword Clue
- Mario Lopez
- Non Fiction Meaning
- Hig Roberts
- Japanese Watch Brands
- Data Driven_0.xml
- Nina Aoulik
- Deacon Johnson
- Sheryl Lowe Age