Theoretical probabilities are fundamental to the field of statistics and mathematics, providing a framework for understanding the likelihood of various outcomes in uncertain situations. From games of chance to scientific experiments, the concept of probability helps us make sense of the randomness that exists in our world. By examining the principles behind theoretical probabilities, we can gain insights into various scenarios and enhance our decision-making processes.
In this article, we will explore what theoretical probabilities are, how they are calculated, and their real-world applications. We will delve into the distinctions between theoretical and experimental probabilities, and address common questions that may arise. Whether you are a student, a professional, or simply someone curious about the world of probabilities, this guide will serve as a valuable resource for enhancing your understanding.
Join us as we embark on a journey through the intriguing world of theoretical probabilities. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer grasp of how probabilities shape our understanding of chance events and the methodologies used to analyze them.
What Are Theoretical Probabilities?
Theoretical probabilities refer to the likelihood of an event occurring based on the possible outcomes in a given scenario, assuming all outcomes are equally likely. This type of probability is derived from mathematical principles rather than empirical data. The formula to calculate the theoretical probability of an event is:
P(E) = Number of favorable outcomes / Total number of possible outcomes
In this equation, P(E) represents the probability of event E occurring. The numerator counts the number of ways that event E can happen, while the denominator counts all possible outcomes in the sample space.
How Are Theoretical Probabilities Calculated?
Calculating theoretical probabilities involves a systematic approach to understanding the possible outcomes of an event. Here are the steps to determine theoretical probabilities:
- Identify the event of interest.
- Determine all possible outcomes of the scenario.
- Count the number of favorable outcomes for the event.
- Apply the theoretical probability formula.
Can You Provide Examples of Theoretical Probabilities?
Certainly! Here are a few examples to illustrate theoretical probabilities:
- Example 1: Rolling a six-sided die. The probability of rolling a 4 is 1/6, as there is one favorable outcome (rolling a 4) and six total possible outcomes (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6).
- Example 2: Flipping a coin. The probability of getting heads is 1/2 since there are two possible outcomes (heads or tails) and one favorable outcome (heads).
- Example 3: Drawing a card from a standard deck of 52 cards. The probability of drawing an Ace is 4/52, as there are four Aces in the deck and 52 total cards.
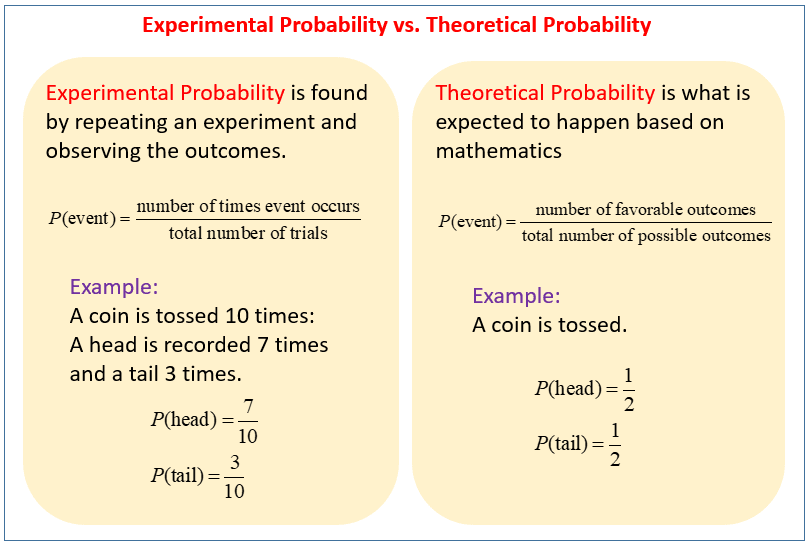
What Is the Difference Between Theoretical and Experimental Probabilities?
Theoretical probability is based on mathematical reasoning, while experimental probability is derived from actual experiments or observations. Here are some key differences:
| Theoretical Probability | Experimental Probability |
|---|---|
| Calculated using formulas and mathematical principles. | Calculated based on the results of experiments or trials. |
| Assumes all outcomes are equally likely. | Reflects the actual outcomes observed in practice. |
| Does not depend on real-world data. | Dependent on the number of trials conducted. |
Why Are Theoretical Probabilities Important?
Theoretical probabilities play a crucial role in various fields, including:
- Statistics: They provide a foundation for statistical analysis and hypothesis testing.
- Finance: They are used to assess risks and make informed investment decisions.
- Science: They help in predicting outcomes of experiments and understanding natural phenomena.
- Games: They are vital in understanding odds in gambling and game strategies.
How Do Theoretical Probabilities Apply to Real Life?
Theoretical probabilities are not just abstract concepts; they find numerous applications in our daily lives. Here are a few examples:
- Weather forecasting relies on probabilities to predict the likelihood of rain or sunshine.
- Insurance companies use probabilities to determine premiums based on risk assessments.
- Sports analysts use probabilities to evaluate team performance and predict game outcomes.
Can Theoretical Probabilities Be Misinterpreted?
Yes, theoretical probabilities can sometimes be misinterpreted. Common pitfalls include:
- Assuming past outcomes influence future events (the gambler's fallacy).
- Miscalculating probabilities due to overlooking possible outcomes.
- Confusing theoretical probabilities with experimental probabilities.
What Are The Limitations of Theoretical Probabilities?
While theoretical probabilities provide valuable insights, they have limitations:
- They assume ideal conditions, which may not exist in real-world scenarios.
- They do not account for biases or external factors that could influence outcomes.
- They may not always accurately predict rare events or extreme outcomes.
In conclusion, understanding what are theoretical probabilities is essential for navigating both academic and practical applications of probability theory. By learning how to calculate and interpret these probabilities, individuals can enhance their decision-making skills and develop a deeper appreciation for the complexities of chance and uncertainty in everyday life.
Article Recommendations
- Hig Roberts
- Non Fiction Meaning
- Lola Consuelos Weight Loss Ozempic
- Efficient Strategies_0.xml
- Madison Beer Nude Leak
- Brand Building_0.xml
- How Old Is Adriana Lima 2024
- Risk Territory Between Ukraine And Siberia Nyt
- Clothes Not Smelling Fresh After Washing
- Digital Revolution_0.xml