AP Bio transcription and translation are fundamental biological processes that play a critical role in gene expression. These processes are essential for the synthesis of proteins in living organisms, and understanding them is crucial for students studying Advanced Placement Biology. In this article, we will explore the intricate details of transcription and translation, how they work, and their significance in cellular biology.
By delving into the mechanisms of transcription and translation, students can gain a deeper appreciation for the molecular biology that underpins life itself. This article aims to provide a thorough understanding of the concepts involved, supported by reliable data and examples. Whether you are preparing for your AP Biology exam or simply interested in learning more about these processes, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need.
From the role of RNA polymerase in transcription to the intricacies of ribosome function during translation, we will cover essential topics that are vital for mastering the subject. So let’s embark on this journey to unravel the fascinating world of AP Bio transcription and translation.
Table of Contents
- What is Transcription?
- Steps of Transcription
- What is Translation?
- Steps of Translation
- Importance of Transcription and Translation
- Differences Between Transcription and Translation
- Common Mistakes in Transcription and Translation
- Conclusion
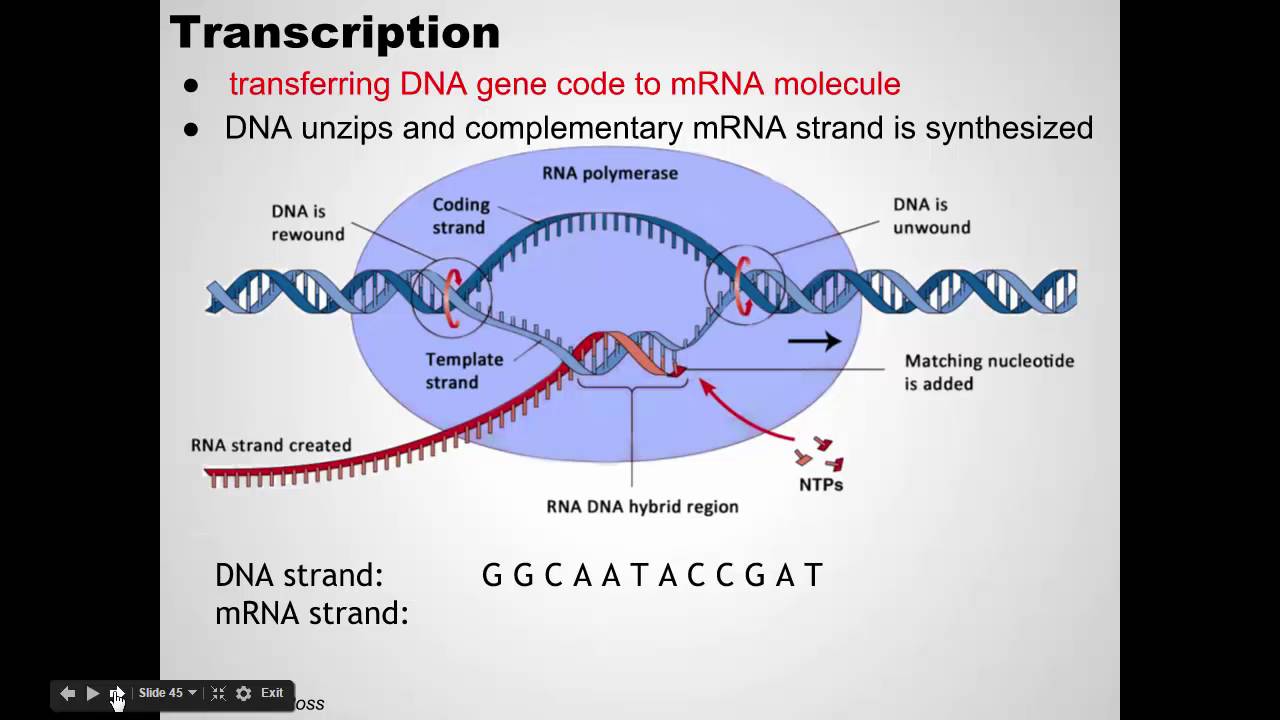
What is Transcription?
Transcription is the first step in the process of gene expression, where the DNA sequence of a gene is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA). This process occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and involves several key components:
- DNA Template: The double-stranded DNA unwinds, and one strand serves as the template for mRNA synthesis.
- RNA Polymerase: An enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of RNA from the DNA template.
- Nucleotides: The building blocks of RNA, which are adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
The end product of transcription is a single-stranded RNA molecule that is complementary to the DNA template strand.
Steps of Transcription
The transcription process involves three main stages:
1. Initiation
During initiation, RNA polymerase binds to a specific region of the DNA called the promoter. This region signals the start of a gene. Once bound, RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA strands, exposing the template strand.
2. Elongation
In the elongation phase, RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template strand, synthesizing mRNA by adding RNA nucleotides complementary to the DNA template. This process continues until a termination signal is reached.
3. Termination
Termination occurs when RNA polymerase encounters a specific sequence in the DNA that signals the end of transcription. The newly synthesized mRNA strand detaches from the DNA, and the DNA strands re-anneal.
What is Translation?
Translation is the second step in the process of gene expression, where the mRNA sequence is decoded by ribosomes to synthesize proteins. This process occurs in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and involves several components:
- Ribosomes: The cellular machinery that facilitates the translation process.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Molecules that transport amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis.
- Amino Acids: The building blocks of proteins, which are linked together to form a polypeptide chain.
Steps of Translation
The translation process can be divided into three main stages:
1. Initiation
During initiation, the small ribosomal subunit binds to the mRNA molecule at the start codon (AUG). The initiator tRNA, carrying the amino acid methionine, binds to the start codon.
2. Elongation
In the elongation phase, tRNA molecules bring specific amino acids to the ribosome according to the codons on the mRNA. The ribosome catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids, creating a growing polypeptide chain.
3. Termination
Termination occurs when the ribosome encounters a stop codon on the mRNA (UAA, UAG, or UGA). This signals the end of protein synthesis, and the completed polypeptide chain is released from the ribosome.
Importance of Transcription and Translation
Transcription and translation are vital processes for cellular function and organismal development. They are responsible for producing the proteins that carry out numerous functions within the cell, including:
- Enzymatic reactions
- Structural support
- Transport of molecules
- Regulation of gene expression
Without these processes, cells would be unable to produce the proteins necessary for life, leading to severe consequences.
Differences Between Transcription and Translation
While transcription and translation are both critical steps in gene expression, they differ in several key aspects:
- Location: Transcription occurs in the nucleus, while translation occurs in the cytoplasm.
- End Products: Transcription produces mRNA, whereas translation results in the formation of proteins.
- Enzymes Involved: RNA polymerase is responsible for transcription, while ribosomes facilitate translation.
Common Mistakes in Transcription and Translation
Students often make several common mistakes when learning about transcription and translation. Here are some of the most frequent errors:
- Confusing RNA and DNA: It's essential to remember that RNA is single-stranded and contains uracil instead of thymine.
- Overlooking the importance of the promoter: The promoter is crucial for initiating transcription, and its sequence can affect gene expression.
- Ignoring post-transcriptional modifications: Eukaryotic mRNA undergoes processing before translation, including the addition of a 5' cap and poly-A tail.
Conclusion
In summary, AP Bio transcription and translation are essential processes that enable gene expression and protein synthesis in living organisms. By understanding the steps involved in each process, students can grasp the fundamental concepts of molecular biology that govern life. We encourage you to explore these topics further, whether through additional reading or practical applications in the lab.
If you found this article helpful, please leave a comment below or share it with your peers. Don’t forget to check out our other articles for more insights into biology and related subjects!
Thank you for visiting, and we hope to see you again for more engaging content on biology and science!
Article Recommendations
- Healthy Habits_0.xml
- Active Smooth Nail Polish
- Dinosaur Dung
- Exterior Joint Compound
- Global Impact_0.xml
- Deacon Johnson
- Girl Meets World Cast
- Convert Excel To Html Table
- Outdoor Propane Heater Table Top
- Cost To Extend Garage