What are the parts of a chemical equation? This is a fundamental question in chemistry that helps us understand the intricate processes that occur during chemical reactions. Chemical equations serve as a symbolic representation of chemical reactions, allowing scientists to convey complex information succinctly. In this article, we will explore the various components of a chemical equation, their significance, and how to interpret them effectively.
As we dive into this topic, we will cover the different parts of a chemical equation, including reactants, products, coefficients, and states of matter. Understanding these components is crucial for students, teachers, and anyone interested in the sciences, as it lays the groundwork for a more profound comprehension of chemical principles and reactions. Whether you are a high school student preparing for exams or a curious learner, this guide aims to enhance your knowledge of chemical equations.
Additionally, we will provide practical examples and insights into how chemical equations are constructed and balanced, contributing to your overall chemistry education. So, let’s embark on this educational journey to uncover the essential parts of chemical equations.
Table of Contents
- 1. Definition of a Chemical Equation
- 2. Parts of a Chemical Equation
- 3. Balancing Chemical Equations
- 4. Examples of Chemical Equations
- 5. Importance of Chemical Equations
- 6. Common Mistakes in Writing Chemical Equations
- 7. Conclusion
1. Definition of a Chemical Equation
A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction, which shows the reactants and products involved. It illustrates how substances interact to form new compounds, emphasizing the conservation of mass, where the total mass of reactants equals the total mass of products.
2. Parts of a Chemical Equation
Understanding the different parts of a chemical equation is essential for interpreting and writing them accurately. Below, we will break down these components:
2.1 Reactants
Reactants are the starting materials in a chemical reaction. They are written on the left side of the equation. For example, in the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen to form water, hydrogen and oxygen are the reactants.
2.2 Products
Products are the substances that are formed as a result of the chemical reaction. They are listed on the right side of the equation. Continuing with the previous example, water is the product of the reaction.
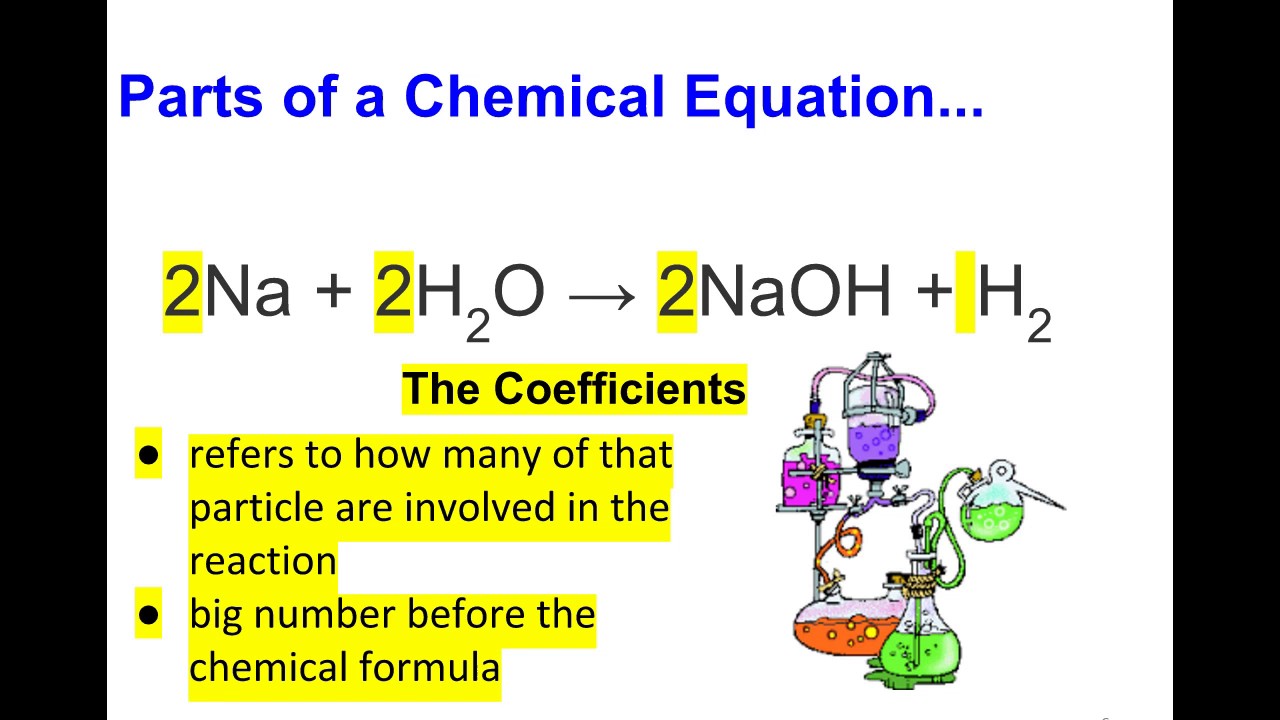
2.3 Coefficients
Coefficients are numerical values placed before the chemical formulas to indicate the number of molecules or moles of a substance involved in the reaction. For instance, in the equation 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O, the coefficient "2" before H₂O indicates that two molecules of water are produced.
2.4 States of Matter
The states of matter of reactants and products are often indicated in parentheses next to their chemical formulas. Common notations include (s) for solid, (l) for liquid, (g) for gas, and (aq) for aqueous solutions. For example, in the equation 2H₂(g) + O₂(g) → 2H₂O(l), the states of matter are clearly defined.
3. Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing a chemical equation is a crucial step in ensuring that the law of conservation of mass is upheld. This process involves adjusting the coefficients to ensure that the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of the equation. For example, in the unbalanced equation H₂ + O₂ → H₂O, there are two oxygen atoms on the left and only one on the right. The balanced equation would be 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O.
4. Examples of Chemical Equations
Let’s take a look at some examples of chemical equations to solidify our understanding of their parts:
- Combustion of Methane: CH₄(g) + 2O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(g)
- Synthesis of Ammonia: N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) → 2NH₃(g)
- Decomposition of Water: 2H₂O(l) → 2H₂(g) + O₂(g)
5. Importance of Chemical Equations
Chemical equations are fundamental for several reasons:
- They provide a clear and concise way to represent chemical reactions.
- They help in predicting the outcomes of reactions and are essential for stoichiometry calculations.
- They are vital in various scientific fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science.
6. Common Mistakes in Writing Chemical Equations
While writing chemical equations, students often make several common mistakes:
- Neglecting to balance the equation properly.
- Omitting states of matter.
- Misrepresenting the chemical formulas of reactants or products.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the parts of a chemical equation is fundamental for anyone studying chemistry. We covered the essential components, including reactants, products, coefficients, and states of matter. Balancing these equations is crucial for accurately representing chemical reactions. We encourage you to practice writing and balancing chemical equations to reinforce your understanding.
We invite you to leave a comment with your thoughts or questions on chemical equations, and don’t forget to share this article with fellow learners who may find it helpful!
Article Recommendations
- Lax Plane Spotting Locations
- Ruben Roman
- Wallet With Pull Tab
- Tumblr Fashion Male
- Nikki Minja Naked
- Nina Aoulik
- How Long Do Horses Live
- Financial Empowerment_0.xml
- Risk Territory Between Ukraine And Siberia Nyt
- Japanese Watch Brands