CPCTC, or Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles are Congruent, is an essential concept in geometry that helps us understand the relationships between triangles. This principle is pivotal in proving the congruence of triangles and establishing relationships in various geometrical problems. In this article, we will delve deep into the concept of CPCTC, providing valuable insights, examples, and applications that will enhance your understanding of this fundamental geometric principle.
Triangles are one of the simplest shapes in geometry, yet they hold significant importance in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and art. By understanding how to prove that two triangles are congruent, we can infer that their corresponding parts are also equal. This article aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to effectively apply CPCTC in solving problems and proving geometric theorems.
Whether you are a student preparing for exams or someone interested in enhancing your knowledge of geometry, this article will serve as a comprehensive resource. We will explore the definition of CPCTC, its applications, and provide you with practical examples to illustrate its importance in geometry.
Table of Contents
- What is CPCTC?
- Importance of CPCTC
- How to Use CPCTC in Proofs
- Examples of CPCTC
- Common Misconceptions About CPCTC
- Applications of CPCTC in Real Life
- Conclusion
- References
What is CPCTC?
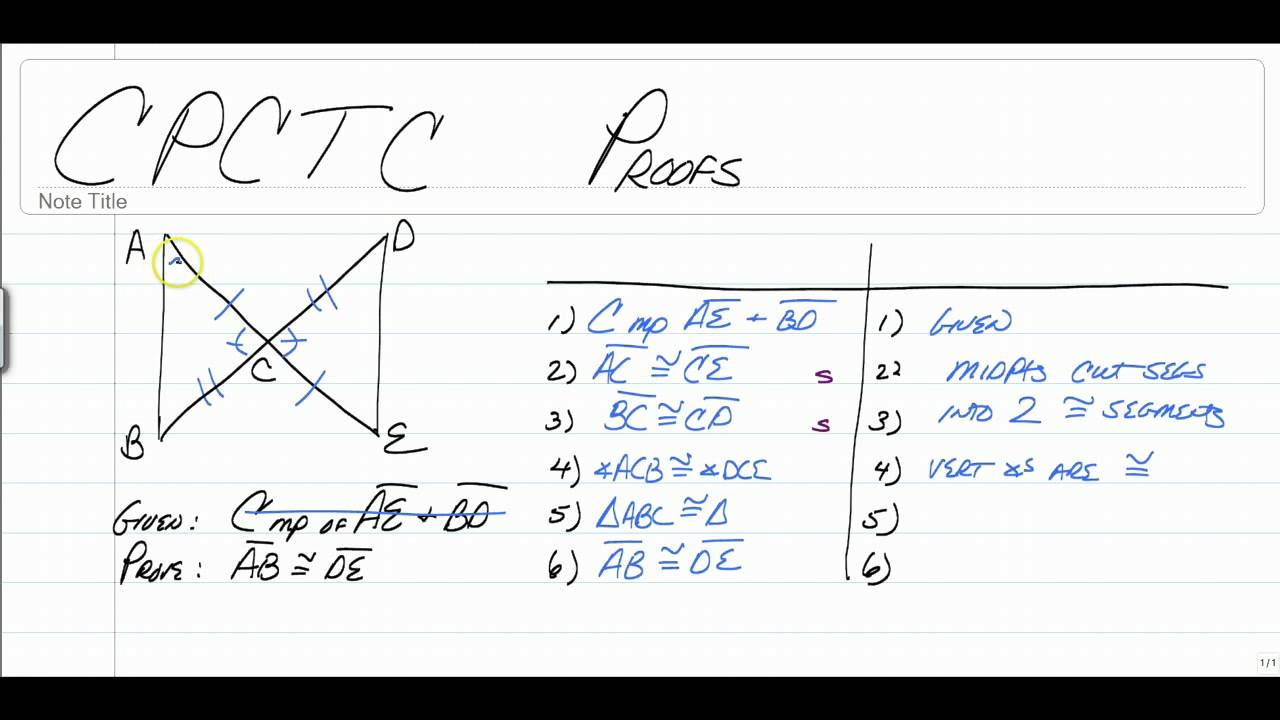
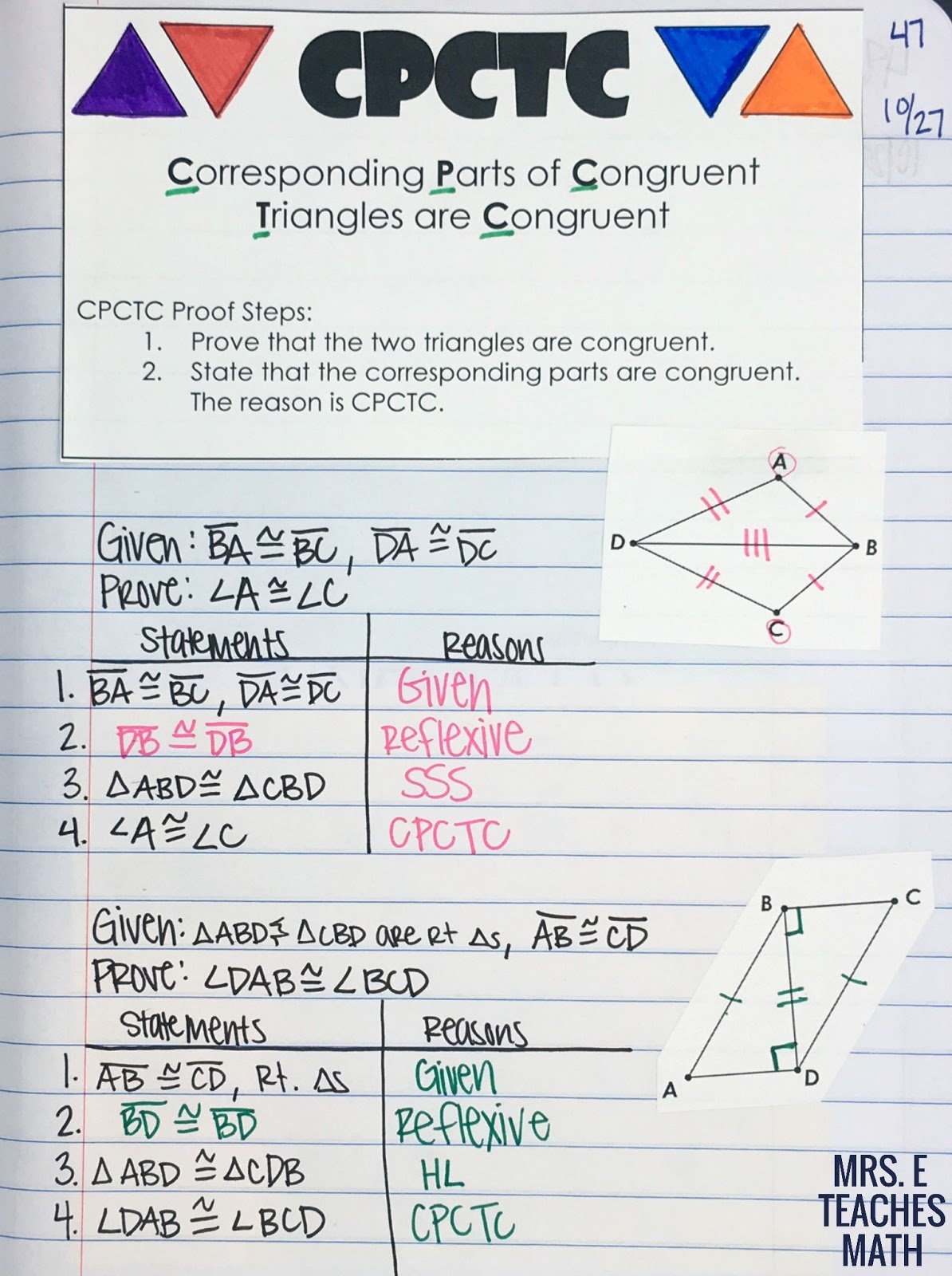
CPCTC stands for Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles are Congruent. It is a theorem used in geometry that states if two triangles are proven to be congruent, then their corresponding parts (sides and angles) are also congruent. This theorem is often the final step in proving that two triangles are congruent after establishing that they meet one of the congruence criteria: SSS (Side-Side-Side), SAS (Side-Angle-Side), ASA (Angle-Side-Angle), AAS (Angle-Angle-Side), or HL (Hypotenuse-Leg for right triangles).
Key Points of CPCTC
- CPCTC applies only after triangles are proven congruent.
- Corresponding parts include sides and angles of the triangles.
- It is essential for solving problems that require the measurement of angles and sides.
Importance of CPCTC
Understanding CPCTC is crucial for several reasons:
- Foundation of Geometry: CPCTC serves as a foundational principle in geometry, allowing students and professionals to establish congruence between shapes.
- Problem-Solving: It is a powerful tool in solving complex geometric problems where the measurement of angles and sides is necessary.
- Proving Theorems: CPCTC is frequently used in geometric proofs, helping to validate the properties of triangles and other shapes.
How to Use CPCTC in Proofs
Utilizing CPCTC in proofs involves a systematic approach:
- Establish that two triangles are congruent using one of the congruence criteria.
- Once congruence is established, you can confidently state that the corresponding parts are also congruent.
- Use this information to solve for unknown angles or sides as necessary.
Examples of CPCTC
Let’s look at some practical examples of how CPCTC is applied:
Example 1: Using SSS Criterion
Consider two triangles, ABC and DEF, where:
- AB = DE = 5 cm
- BC = EF = 7 cm
- AC = DF = 9 cm
Since all three sides in triangle ABC are equal to the corresponding sides in triangle DEF, we can conclude that triangle ABC is congruent to triangle DEF (by SSS). Therefore, we can apply CPCTC, stating that:
- ∠A = ∠D
- ∠B = ∠E
- ∠C = ∠F
Example 2: Using ASA Criterion
Consider two triangles, GHI and JKL, where:
- ∠G = ∠J = 30°
- ∠H = ∠K = 70°
- GH = JK = 6 cm
With two angles and the included side equal, we can conclude that triangle GHI is congruent to triangle JKL (by ASA). Using CPCTC, we can then state:
- GI = JL
- HI = KL
Common Misconceptions About CPCTC
There are several common misconceptions regarding CPCTC that are important to clarify:
- CPCTC can only be used after proving triangle congruence; it cannot be used independently.
- Corresponding parts must be clearly identified; failing to do so can lead to incorrect conclusions.
- CPCTC applies only to triangles, not to any other geometric shapes.
Applications of CPCTC in Real Life
CPCTC is not just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in various fields:
- Architecture: Architects use CPCTC to ensure that structural components fit together correctly.
- Engineering: Engineers apply CPCTC in designing components that must meet specific geometric criteria.
- Art: Artists may use principles of congruence to create symmetrical designs.
Conclusion
In summary, CPCTC is a fundamental concept in geometry that revolves around the congruence of triangles and their corresponding parts. Understanding this principle is crucial for solving geometric problems and proving theorems. By mastering CPCTC, students and professionals alike can enhance their problem-solving skills and apply these concepts in real-world scenarios. We encourage you to explore more about geometry, practice problems, and share your experiences in the comments below!
References
- Euclid, "Elements," Translated by Thomas Heath.
- Smith, David E. "History of Mathematics."
- Hall, H. S., & Knight, F. H. "Higher Algebra."
Article Recommendations
- Lax Plane Spotting Locations
- Balanced Lifestyle_0.xml
- Claudine Blanchard Crimes
- Metal Worker
- Career Advancement_0.xml
- Deacon Johnson
- Mia Hamm Soccer Player
- Ne Yo
- Galaxy Playdough
- Ella Bleu S Career Updates