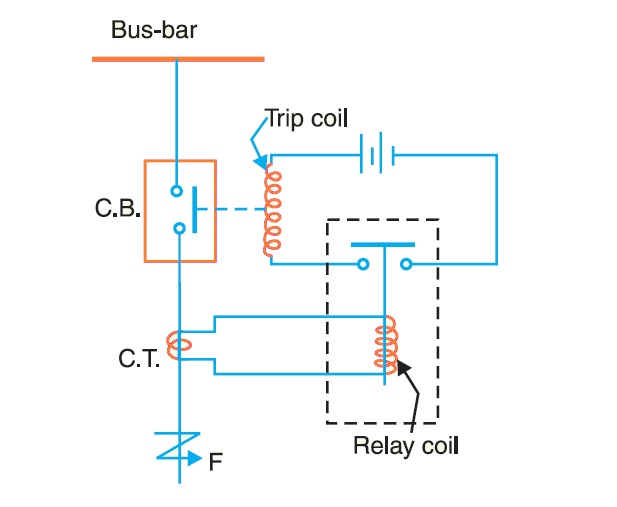
Understanding how an electrical relay works is crucial for anyone interested in electronics or electrical engineering. This component plays a pivotal role in controlling electrical circuits, making it an essential part of many devices we use daily. In this article, we will delve into the workings of electrical relays, their types, applications, and much more. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of electrical relays and their significance in modern technology.
Electrical relays are electromagnetic switches that allow a low-power signal to control a much larger current flow. They are used in various applications, from simple household devices to complex industrial systems. As we explore the intricacies of electrical relays, we will also look at their components, types, and practical applications to provide you with a well-rounded perspective on this vital electronic component.
Whether you are an electronics enthusiast, a student, or a professional in the field, this guide will serve as a valuable resource. With a clear explanation of how electrical relays function, along with diagrams and examples, you will gain insights that can enhance your understanding and skills in electronics.
Table of Contents
- What is a Relay?
- How Do Relays Work?
- Types of Relays
- Applications of Relays
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Safety Considerations
- Conclusion
What is a Relay?
An electrical relay is an electromagnetic switch that is used to control a circuit. By using a small amount of electrical energy, a relay can control a larger electrical load. In simpler terms, it acts as a middleman between a low-power signal and a high-power circuit, allowing the low-power signal to switch the high-power circuit on or off.
Components of a Relay
- Coil: The coil is the electromagnet that converts electrical energy into magnetic energy.
- Armature: The armature is a movable component that makes or breaks the circuit when the coil is energized.
- Contacts: These are the conductive parts that open or close the circuit.
- Spring: The spring returns the armature to its original position when the coil is de-energized.
How Do Relays Work?
The operation of an electrical relay is relatively straightforward. When a current flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field that attracts the armature. This action closes the contacts, allowing current to flow through the circuit. When the current to the coil is interrupted, the spring pulls the armature back, opening the contacts and stopping the current flow.
Step-by-Step Process
- The coil is energized by an external voltage source.
- The magnetic field generated by the coil attracts the armature.
- The armature moves, closing the contacts and completing the circuit.
- When the coil is de-energized, the magnetic field collapses.
- The spring returns the armature to its original position, opening the contacts.
Types of Relays
Electrical relays come in various types, each designed for specific applications and operating principles. Understanding these types can help you choose the right relay for your project.
Electromechanical Relays
Electromechanical relays use an electromagnetic coil to operate. They are the most common type of relay and can switch high voltages and currents. These relays are often used in automotive applications, home appliances, and industrial equipment.
Solid State Relays
Solid-state relays (SSRs) use semiconductor devices to switch circuits without moving parts. They offer faster switching times and longer operational life compared to electromechanical relays. SSRs are commonly used in applications where silent operation and high reliability are essential.
Reed Relays
Reed relays are a type of electromechanical relay that uses reed switches to control the circuit. They are compact and can switch low power signals efficiently. Reed relays are often found in telecommunications and automotive applications.
Time Delay Relays
Time delay relays provide a delay before the circuit is activated or deactivated. This feature is useful in applications where timing is critical, such as in HVAC systems or lighting controls.
Applications of Relays
Relays are used in a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some common uses:
- Automotive: Relays are used to control headlights, horn, and other electrical components.
- Home Appliances: Devices like washing machines and refrigerators use relays for various functions.
- Industrial Automation: Relays control motors, pumps, and other heavy machinery.
- Telecommunications: Relays are used in telephone systems for switching purposes.
- HVAC Systems: Relays help in controlling heating and cooling systems efficiently.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
While relays are generally reliable, they can encounter issues that may affect their performance. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting tips:
- Relay Does Not Activate: Check the coil voltage and connections.
- Contacts Welded Together: This may occur due to excessive current. Consider using a relay with higher ratings.
- Intermittent Operation: Inspect for loose connections or damaged components.
Safety Considerations
When working with electrical relays, it's essential to adhere to safety guidelines:
- Always disconnect power before working on electrical circuits.
- Use relays with appropriate voltage and current ratings for your application.
- Handle components with care to avoid damage.
Conclusion
Understanding how an electrical relay works is fundamental for anyone involved in electronics. Relays are versatile components that play a crucial role in controlling electrical circuits across various applications. Whether you are working on a small project or a large industrial system, knowing how to select and troubleshoot relays can enhance your efficiency and effectiveness.
We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments section below. If you found this article helpful, consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. For more insightful articles on electronics and technology, feel free to explore our website.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to welcoming you back for more enlightening content!
Article Recommendations
- Kylie Jenner Before Surgery
- Cost To Extend Garage
- How To Make Raphael In Infinite Craft
- Corinne Foxx
- How Tall Sarah Jessica Parker
- Light Therapy
- Global Impact_0.xml
- Lava Stone Bracelet Essential Oil
- Brand Building_0.xml
- Personal Wifi