The location of protons in an atom is a fundamental aspect of atomic structure that plays a crucial role in understanding chemical properties and behavior. Protons, which are positively charged particles, reside in the nucleus of an atom alongside neutrons. Their arrangement and interaction with electrons determine the chemical identity and reactivity of an element. In this article, we will explore the significance of protons, their role in atomic structure, and how they influence various chemical properties.
In the realm of atomic physics, understanding the location of protons is essential for grasping the principles of chemistry and physics. The position of protons within the nucleus impacts the overall charge of the atom, which in turn affects how it interacts with other atoms. This article aims to provide in-depth knowledge about protons, their location, and how they contribute to the properties of matter.
As we delve deeper into the topic, we will cover various aspects related to protons, including their definition, characteristics, and the role they play in the formation of different elements. We will also discuss the implications of proton location on atomic stability and reactivity. By the end of this article, readers will gain a thorough understanding of the location of protons in atoms and their significance in the broader context of chemistry.
Table of Contents
- Definition of Protons
- Structure of an Atom
- Location of Protons in Nucleus
- Role of Protons in Chemical Properties
- Proton Number and Atomic Identity
- Neutron and Proton Interaction
- Protons and Electrons
- Conclusion and Implications
Definition of Protons
Protons are subatomic particles found within the atomic nucleus. They carry a positive electric charge of +1 elementary charge and have a relative mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu). Protons are one of the three primary components of atoms, alongside neutrons (neutral charge) and electrons (negative charge). The presence of protons in the nucleus determines the atomic number of an element, which is crucial for identifying the element itself and its position on the periodic table.
Structure of an Atom
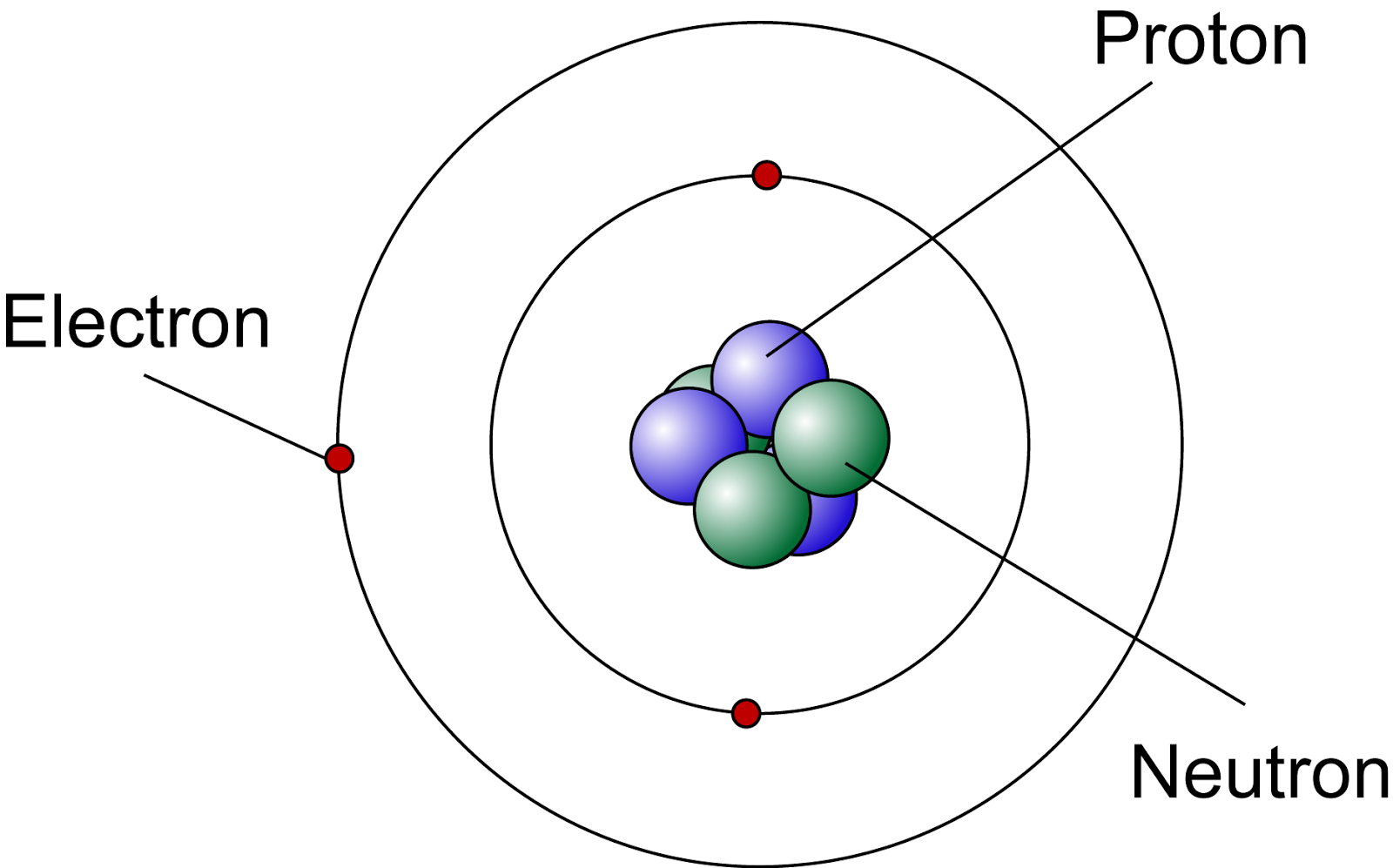
An atom consists of a central nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons, which are held together by the strong nuclear force. The arrangement and number of these particles dictate the atom's overall stability and behavior. The electrons occupy specific energy levels or orbitals around the nucleus, and their arrangement affects how the atom interacts with other atoms during chemical reactions.
Components of an Atom
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the nucleus.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles also found in the nucleus, contributing to the atomic mass.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in defined energy levels.
Location of Protons in Nucleus
Protons are exclusively located within the nucleus of an atom. The nucleus is situated at the center of the atom and is densely packed with protons and neutrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is equal to the atomic number of the element, which defines its identity. For instance, an atom with one proton is hydrogen, while an atom with six protons is carbon. The protons are held together in the nucleus by the strong nuclear force, which overcomes the electrostatic repulsion between the positively charged protons.
Role of Protons in Chemical Properties
The number of protons in an atom significantly influences its chemical properties. This is because protons determine the atomic number, which in turn affects the atom's electronic configuration and its behavior during chemical reactions. Atoms with the same number of protons exhibit similar chemical properties, forming groups in the periodic table known as elements.
Influence on Atomic Stability
The stability of an atom is closely related to the ratio of protons to neutrons within the nucleus. An optimal balance between these particles contributes to nuclear stability, while an imbalance can lead to radioactive decay or instability. The presence of additional neutrons can sometimes stabilize a nucleus, allowing for the existence of isotopes.
Proton Number and Atomic Identity
The atomic number is defined as the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It is a fundamental property that uniquely identifies an element. For example:
- Hydrogen: 1 proton (atomic number 1)
- Oxygen: 8 protons (atomic number 8)
- Gold: 79 protons (atomic number 79)
Elements are organized in the periodic table based on their atomic number, and this organization reflects trends in chemical behavior and properties.
Neutron and Proton Interaction
Neutrons play a crucial role in the stability of the nucleus by affecting the strong nuclear force that holds protons together. While protons repel each other due to their positive charges, neutrons provide additional attractive forces that help stabilize the nucleus. The balance between neutrons and protons determines whether an atom will be stable or undergo radioactive decay.
Protons and Electrons
Protons are closely associated with electrons, which orbit the nucleus. The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons, giving the atom an overall neutral charge. The arrangement of electrons in energy levels affects the atom's chemical reactivity and bonding behavior. Atoms can gain or lose electrons through chemical reactions, but the number of protons remains constant, thereby preserving the identity of the element.
Conclusion and Implications
In conclusion, the location of protons in an atom is a fundamental aspect of atomic structure that influences the atom's identity, stability, and chemical properties. Understanding the role of protons enhances our knowledge of chemical behavior and is essential for various scientific fields, including chemistry, physics, and materials science. As we continue to explore atomic structures, the significance of protons remains at the forefront of our understanding of matter.
We encourage readers to engage with this topic further by leaving comments, sharing this article, or exploring additional resources related to atomic structure and chemistry.
Thank you for taking the time to read this article. We hope you found it informative and thought-provoking. Don’t forget to visit us again for more insights into the fascinating world of science!
Article Recommendations
- Jeremy Wariner Net Worth
- Kamila Valieva
- Ne Yo
- Clothes Not Smelling Fresh After Washing
- Corinne Foxx
- Arianna Lima 2024
- Brand Building_0.xml
- Kylie Jenner Before Surgery
- Legal Seafood Recipes Crab Cakes
- Wallet With Pull Tab