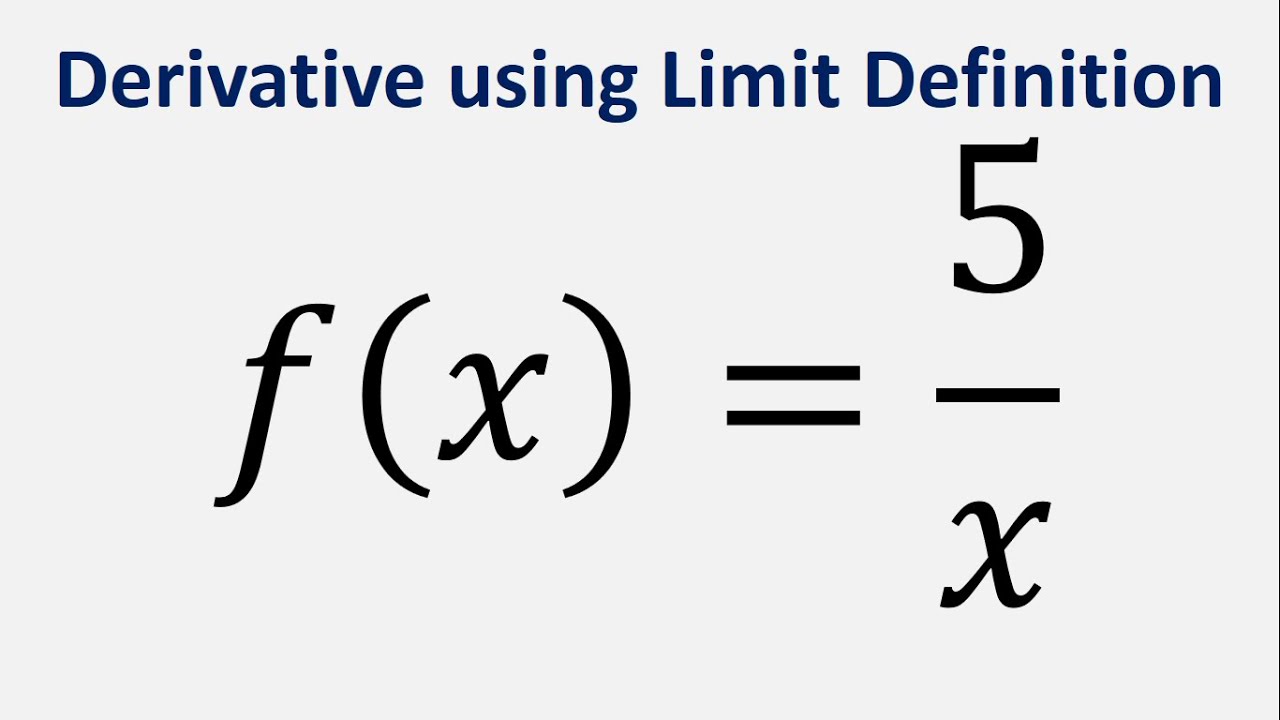The concept of derivatives is a fundamental aspect of calculus that allows us to understand how functions change. One intriguing function to analyze is the derivative of 5/x, a rational function that presents unique characteristics in its behavior. Understanding how to determine the derivative of this function not only enhances our grasp of calculus but also opens the door to various applications in mathematics and real-world scenarios. As we delve into this topic, we will explore how to compute the derivative of 5/x, its significance, and some practical examples to solidify our understanding.
In calculus, the derivative of a function at a given point measures the function's rate of change at that point. The derivative of 5/x, in particular, serves as an excellent example for students and professionals alike, demonstrating the application of the power rule and quotient rule in differentiation. By breaking down the steps of calculating this derivative, we can better appreciate the intricacies of calculus.
As we navigate through the process, we will also address common questions that arise when dealing with derivatives, such as how the derivative of 5/x behaves as x approaches different values and its graphical representation. By the end of this article, you will not only be equipped with the knowledge to compute the derivative but also understand its broader implications in various fields including physics, engineering, and economics.
What is the Derivative of 5/x?
The derivative of a function can be found using several rules in calculus. For the function 5/x, we can express it in a form that makes differentiation easier. We can rewrite 5/x as 5 * x^(-1). This allows us to apply the power rule of derivatives effectively.
How Do You Differentiate 5/x Using the Power Rule?
To differentiate the function 5/x, we can utilize the power rule. The power rule states that if you have a function in the form of x^n, its derivative is n * x^(n-1). Here’s how to apply it step by step:
- Rewrite the function: 5/x = 5 * x^(-1).
- Apply the power rule: The derivative of 5 * x^(-1) is 5 * (-1) * x^(-2).
- Simplify: This results in -5/x^2.
Thus, the derivative of 5/x is -5/x^2. This result provides important information about how the function behaves as x changes.
What Does the Derivative of 5/x Tell Us About the Function?
The derivative of 5/x, which is -5/x^2, indicates that the function is decreasing for all positive values of x. The negative sign implies that as x increases, the value of 5/x decreases. Moreover, the rate of decrease becomes more pronounced as x moves closer to zero.
Why Is the Derivative of 5/x Important in Calculus?
Understanding the derivative of 5/x is crucial for several reasons:
- It helps identify critical points where the function may have local maxima or minima.
- It illustrates the concept of limits and the behavior of functions as they approach certain values.
- It serves as a building block for more complex calculus concepts such as integration and differential equations.
How Can You Graph the Derivative of 5/x?
Graphing the function 5/x alongside its derivative -5/x^2 can provide visual insights into their relationship. Here are the steps to graph these functions:
- First, plot the function 5/x. Note that it approaches infinity as x approaches zero from the right and approaches zero as x goes to infinity.
- Next, plot the derivative -5/x^2. This function will always be negative, indicating that 5/x is decreasing throughout its domain.
- Observe how the slope of the tangent line to the curve of 5/x changes as you move along the graph.
What Are Some Applications of the Derivative of 5/x?
The derivative of 5/x has various applications across different fields:
- In physics, it can be used to determine the velocity of an object moving inversely to time.
- In economics, it helps analyze cost functions and optimize pricing strategies.
- In engineering, it assists in modeling relationships between different variables in design processes.
Can You Find the Derivative of 5/x at a Specific Point?
Yes, you can find the derivative of 5/x at any given point by substituting the x-value into the derivative function -5/x^2. For instance, if you want to find the derivative at x = 2:
- Substituting x = 2 into -5/x^2 gives -5/(2^2).
- This simplifies to -5/4.
Thus, the derivative of 5/x at x = 2 is -5/4, indicating the rate of change of the function at that specific point.
Conclusion: Mastering the Derivative of 5/x
In conclusion, understanding the derivative of 5/x is pivotal for anyone studying calculus. Through the application of the power rule and exploring its implications, we gain valuable insights into the behavior of rational functions. The derivative of 5/x not only serves as a useful mathematical tool but also provides a gateway to deeper concepts in mathematics and its applications in various fields. By mastering this derivative, you enhance your analytical skills and prepare yourself for more advanced topics in calculus and beyond.
Article Recommendations
- Galaxy Playdough
- Data Driven_0.xml
- Jennifer Syme Crash
- Financial Empowerment_0.xml
- Exterior Joint Compound
- Light Therapy
- Daryl Hannah
- Convert Excel To Html Table
- Global Impact_0.xml
- Bryan Hearne