Flip sign inequality is a crucial concept in mathematics that plays a significant role in solving inequalities and understanding their properties. Whether you are a student grappling with algebra or a professional dealing with equations and inequalities, grasping this principle is essential. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of flip sign inequality, its applications, and the underlying rules that govern this mathematical phenomenon.
In the world of mathematics, inequalities are statements that express the relationship between two expressions, indicating if one is less than or greater than the other. When manipulating these inequalities, it's vital to understand when and how to flip the sign, which can impact the solution significantly. This guide aims to provide clarity on this topic, breaking down complex ideas into digestible information.
We will delve into various aspects of flip sign inequality, including its definition, rules, examples, and practical applications. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of how to apply this concept effectively in mathematical problems. Let's embark on this journey to enhance your knowledge and skills in dealing with inequalities.
Table of Contents
- Definition of Flip Sign Inequality
- Rules of Flip Sign Inequality
- Examples of Flip Sign Inequality
- Applications of Flip Sign Inequality
- Common Mistakes in Flip Sign Inequality
- Visual Representation of Inequalities
- Practice Problems
- Conclusion
Definition of Flip Sign Inequality
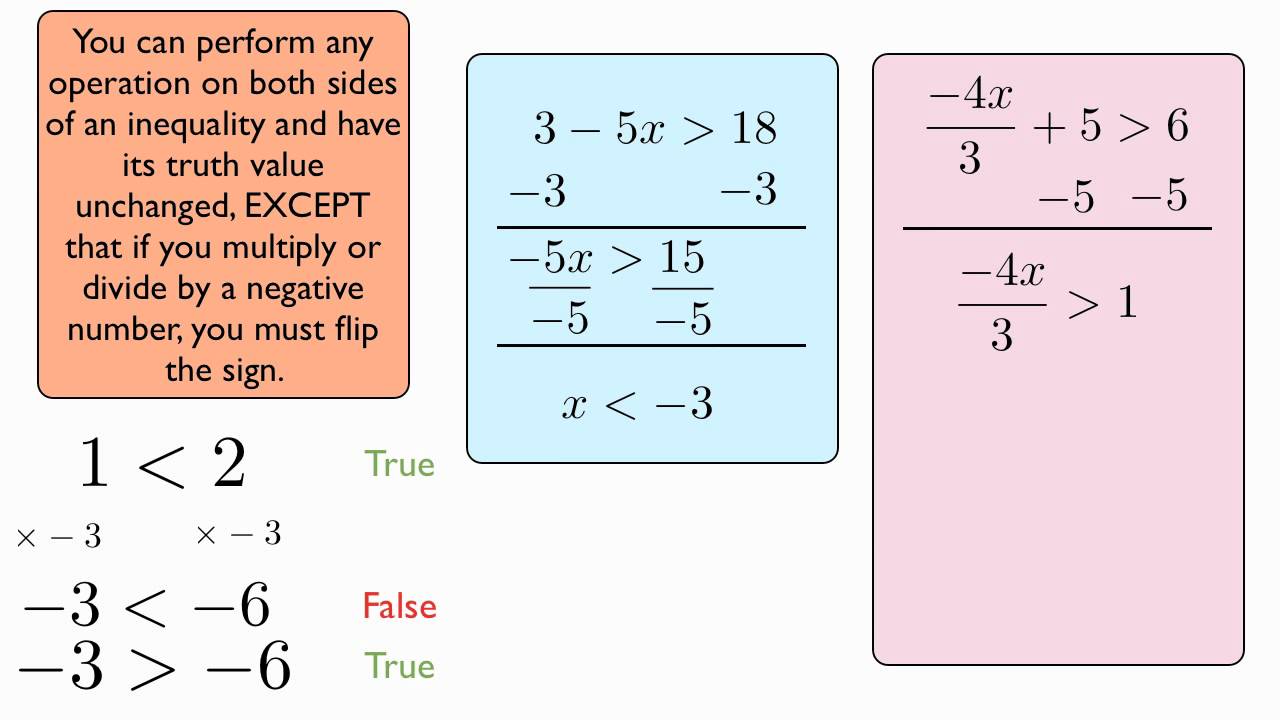
Flip sign inequality refers to the process of reversing the inequality sign when multiplying or dividing both sides of an inequality by a negative number. This action is crucial because it preserves the truth of the inequality.
For example, if we have the inequality:
-2x > 4,
When we divide both sides by -2, the inequality sign flips:
x < -2.
Rules of Flip Sign Inequality
Understanding the rules of flip sign inequality is essential to avoid common pitfalls when solving mathematical problems. Here are the key rules to remember:
- Multiplication Rule: If you multiply or divide both sides of an inequality by a positive number, the direction of the inequality remains unchanged.
- Flip Rule: If you multiply or divide both sides of an inequality by a negative number, the direction of the inequality sign must be flipped.
- Adding/Subtracting Rule: Adding or subtracting the same number from both sides of an inequality does not change the direction of the inequality.
Examples of Flip Sign Inequality
To illustrate the concept of flip sign inequality further, let's look at some examples:
Example 1: Simple Inequality
Consider the inequality:
-3x < 9.
When we divide both sides by -3, we must flip the sign:
x > -3.
Example 2: Complex Inequality
Let's take a more complex example:
2 - 5x > 8.
Subtract 2 from both sides:
-5x > 6.
Now, divide by -5 and flip the sign:
x < -\frac{6}{5}.
Applications of Flip Sign Inequality
Flip sign inequality is widely used in various mathematical applications, including:
- Algebra: Solving linear inequalities in algebraic equations.
- Calculus: Understanding limits and behavior of functions.
- Economics: Analyzing demand and supply inequalities.
- Statistics: Evaluating probabilities and distributions.
Common Mistakes in Flip Sign Inequality
When working with inequalities, it's easy to make mistakes. Here are some common errors to watch out for:
- Not flipping the sign when multiplying or dividing by a negative number.
- Ignoring the rules of addition and subtraction on both sides of the inequality.
- Misinterpreting the results of complex inequalities.
Visual Representation of Inequalities
Visual aids can help in understanding inequalities better. The number line is a useful tool for representing inequalities graphically:
- Open circles indicate that the endpoint is not included (e.g., x < 3).
- Closed circles indicate that the endpoint is included (e.g., x ≤ 3).
Understanding these representations can clarify the solutions to inequalities.
Practice Problems
To reinforce your understanding, here are some practice problems:
- Solve the inequality: -4x + 8 < 0.
- Solve the inequality: 3 - 2x > 7.
- Solve the inequality: -6x - 3 ≤ 15.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding flip sign inequality is crucial for anyone dealing with mathematical inequalities. By mastering the rules and applications of this concept, you can solve inequalities accurately and avoid common mistakes. Remember to practice regularly and refer back to the rules as needed.
We encourage you to leave your comments below, share this article with others who may benefit, and explore more articles on our site for further learning!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back soon for more insightful content!
Article Recommendations
- Healthy Habits_0.xml
- Ne Yo
- How Old Is Adriana Lima 2024
- Sheryl Lowe Age
- Corinne Foxx
- Nina Aoulik
- Japanese Watch Brands
- Water Softener Overflowing Brine Tank
- Wallet With Pull Tab
- Lola Consuelos Weight Loss Ozempic